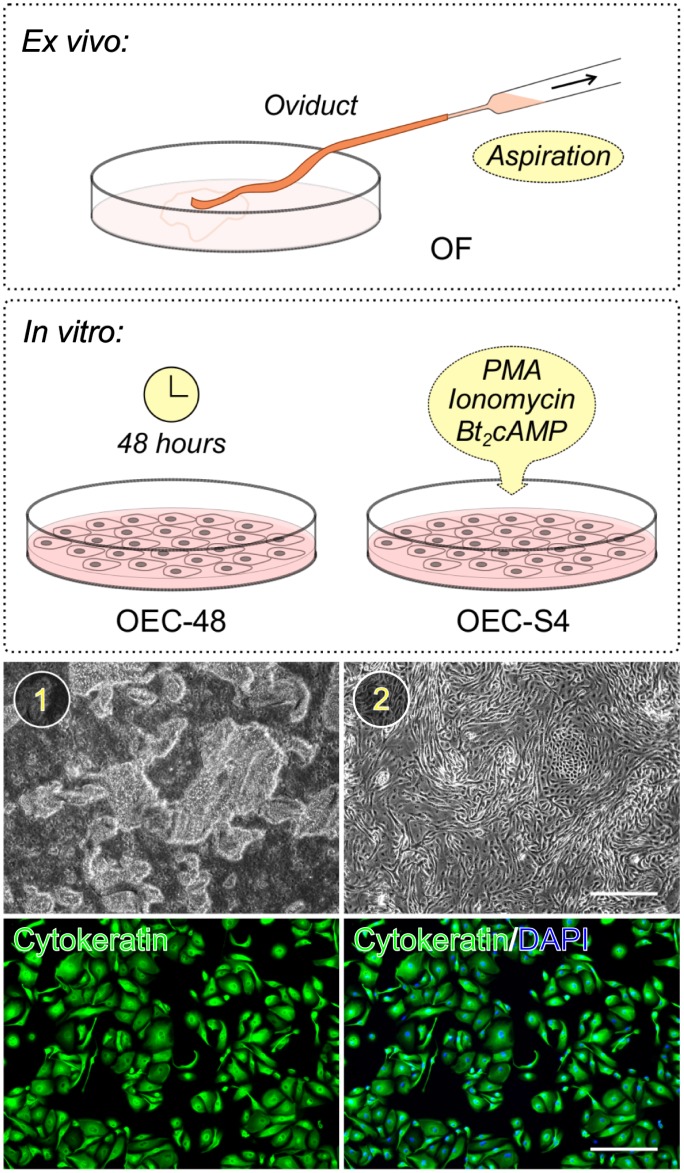
Fig 1. Collection of oviductal cell secretions.
Oviducts were dissected and removed from the mesosalphinx and fluid was collected either by direct aspiration (ex vivo) or after the culture of the oviductal epithelium (in vitro). Media used for culturing oviductal epithelial cells (OECs) were collected after passive conditioning for 48 hours or after a 4-hour stimulation with phorbol myristate acetate (PMA), ionomycin and dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate (Bt2cAMP). (1) Extruded oviductal mucosa containing intact epithelial sheets. (2) Representative image showing attachment and growth of the oviductal epithelial cells after 2–3 days in culture (Scale bar 300 μm). Immunohistochemistry for cytokeratin as a marker for OECs showed that the cultures established by this method were of high purity (Scale bar 200 μm).