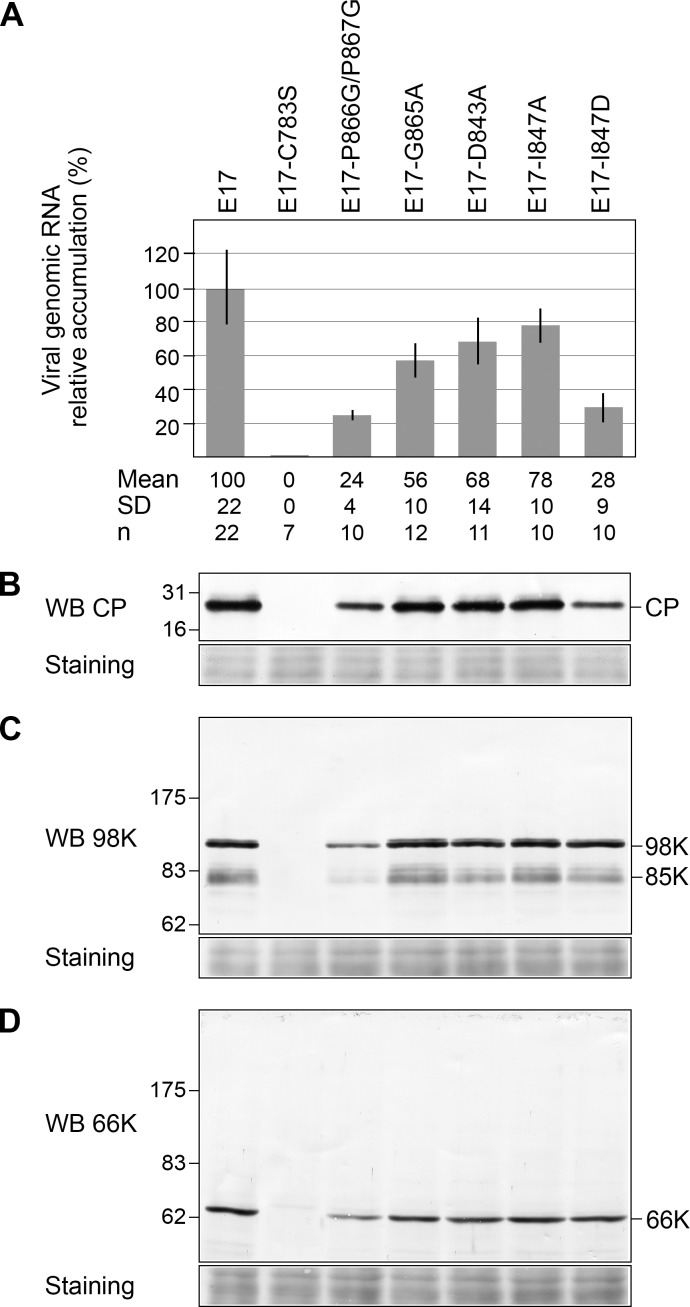
Fig 6. Impact of DUB activity on viral infectivity in Arabidopsis protoplasts.
Arabidopsis protoplasts were transfected with in vitro transcripts as indicated and cells were harvested 48 hpt. (A) The ability of the transcripts to replicate was assessed by extracting total RNAs and quantifying viral genomic RNA by RTqPCR. Viral RNA levels were calibrated and normalized to EF1αανγПΔФ2 and PDF2 reference genes RNAs. The relative accumulation of viral mutant RNAs as compared to the WT TYMV RNA is represented as the mean +/- SD. Mean and SD values, as well as the number of samples (n) analyzed in at least two independent experiments are indicated below panel (A). (B) The ability of the transcripts to replicate was assessed by immunoblotting with anti-CP antibodies. (C) and (D) Detection of mature viral proteins produced during infection. The same samples as in panel (B) were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-98K (C) and anti-66K (D) antibodies. Ponceau staining of the membrane (staining) indicates protein loading. Each mutant was analyzed in two independent experiments.