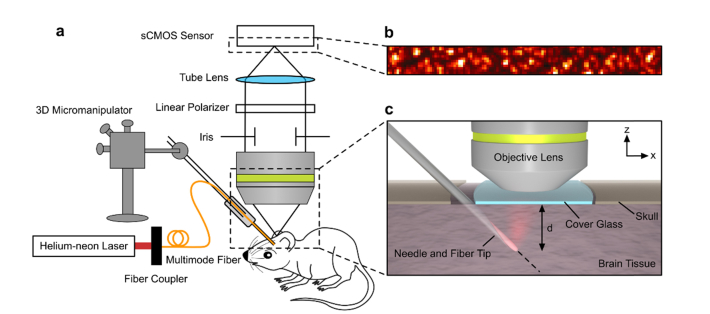
Fig. 1.
Diagram of the experimental setup. (a) The experimental setup consisted of a Helium-neon laser coupled to a custom-made fiber probe. The fiber probe was covered with white ZnO paint to simulate a diffuse point-like source in the tissue. (b) The speckle pattern on the surface of the brain was imaged to an sCMOS sensor using a microscope objective and tube lens. A linear polarizer helped to maximize the contrast of the captured speckle pattern, and the iris ensured an adequate speckle size on the sensor. (c) A zoomed view of the mouse brain and fiber tip. The fiber tip was inserted at a 45-degree angle into the mouse brain through a gap between the skull and the cover glass which formed the cranial window. Then, the fiber was advanced from a depth d of 1.1 mm to 3.2 mm below the brain surface, and a series of speckle patterns were recorded at each depth to analyze the decorrelation time.