Fig. 3.
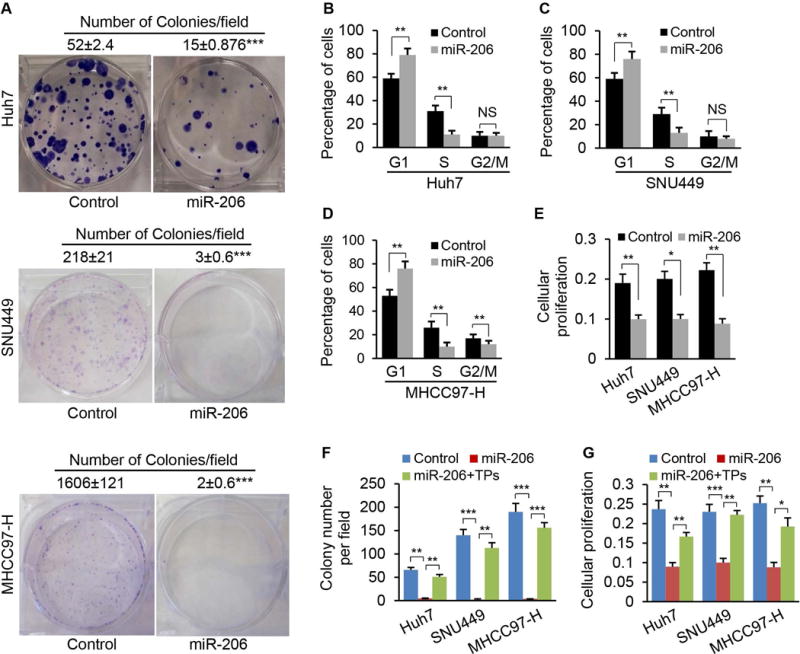
miR-206 prevented colony formation, proliferation and cell cycle progression of human HCC cell lines with divergent backgrounds. (A) Soft agar colony formation assay of Huh7, SNU449 and MHCC97-H cells stably transfected with Plenti-CMV-puromycin-miR-206 or empty plasmids (Control). The numbers represented the average colony numbers of three areas per plate. (B–D) Increased the number of cells in the G1 phase but decreased the number of cells in the S phase. Huh7, SNU449 and MHCC97-H cells were stably transfected with Plenti-CMV-puromycin-miR-206 or empty plasmids (Control). (E) Reduced proliferation of Huh7, SNU449 and MHCC97-H cells after stably transfected with Plenti-CMV-puromycin-miR-206, as revealed by MTT assay. (F–G) TPs of CCND1, cMET, and CDK6 treatment recovered colony formation and proliferation of Huh7, SNU449 and MHCC97-H cells. Huh7, SNU449 and MHCC97-H cells stably transfected with Plenti-CMV-puromycin-miR-206 were treated with TP of CCND1, cMET and CDK6 (20 nM). The Huh7, SNU449 and MHCC97-H cells treated with scramble served as the control (20 nM). NS: no significance. Data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; and ***p < 0.001.
