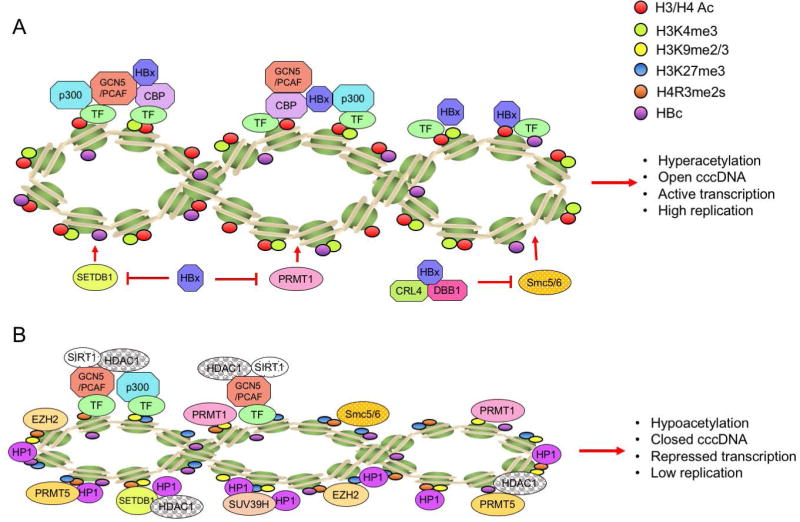
Fig 3. Schematic representation of modification status of HBV cccDNA-assoicated histones and the recruitment of chromatin modifying enzymes on cccDNA in relation to HBx.
(A) In the presence of HBx, cccDNA-bound histones are hyperacetylated, viral minichromosome is in an open configuration and viral gene transcription is activated, leading to a high level of virus replication. (B) In the absence of HBx, host restriction factors, such as Smc5/6 complex and PRMT1, are loaded on cccDNA. The cccDNA-bound histones are hypoacetylated, viral minichromosome is in a closed configuration and viral gene is transcriptionally repressed, resulting in a low level of virus replication. (Abbreviations: H3/H4 Ac, aceylated histone 3 and 4; CBP, CREB-binding protein; PCAF, p300/CBP-associated factor; PRMT1, protein arginine methyltransferase 1 PRMT5, protein arginine methyltransferase 5; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; HDAC1, histone deaceyltransferase 1; EZH2, enhancer of zeste homolog 2; SUV39H, suppressor of variegation 3–9 Homolog; HP1: heterochromatin protein 1 factors; SETDB1: SET Domain Bifurcated 1. Smc5/6: Structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 5/6.)