Figure 8.
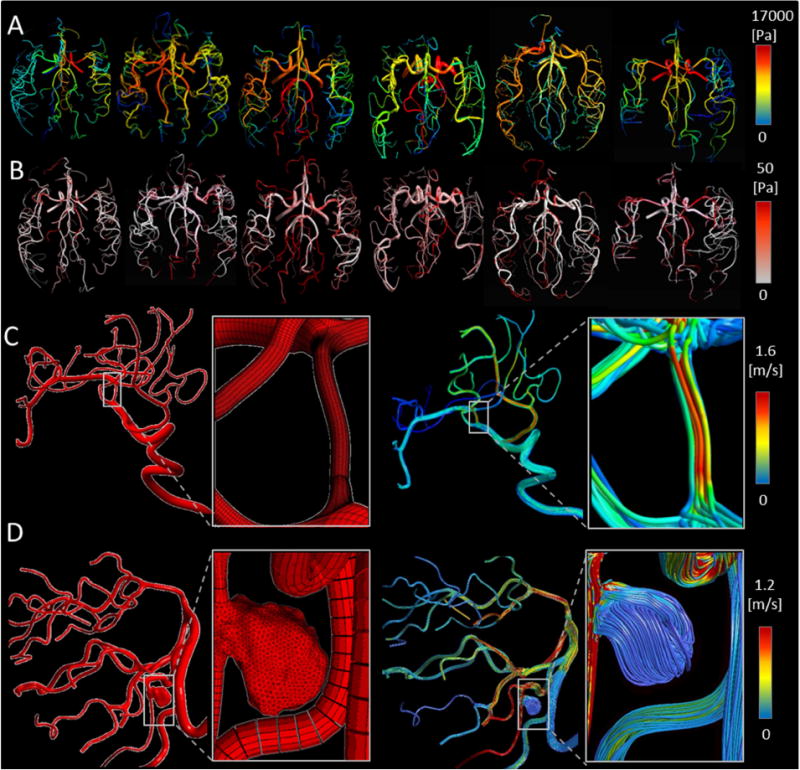
Preliminary 3D hemodynamic CFD analysis using parametric meshes in healthy and pathological cerebral arterial trees. (A) Predicted 3D pressure field for a large portion of cerebral arterial tree simulation at peak-systole in six volunteers. (B) Predicted wall shear stress distribution. (C–D) Hemodynamic simulation in patients with endovascular pathologies. Panel (C) illustrates the application of PRM method for a patient with MCA stenosis. Panel (D) summarizes results for a saccular aneurysm in the vertebral artery. It shows unstructured mesh for a saccular aneurysm in the right vertebral arteries fused to a parametric mesh of the vertebrobasilar system down to posterior cerebral arteries. The magnified insert depicts the hybrid mesh of unstructured aneurysm with parametric vascular tree meshes. The blood flow streamlines are shown for both stenosis and aneurysm pathological cases (right column of C and D panel).
