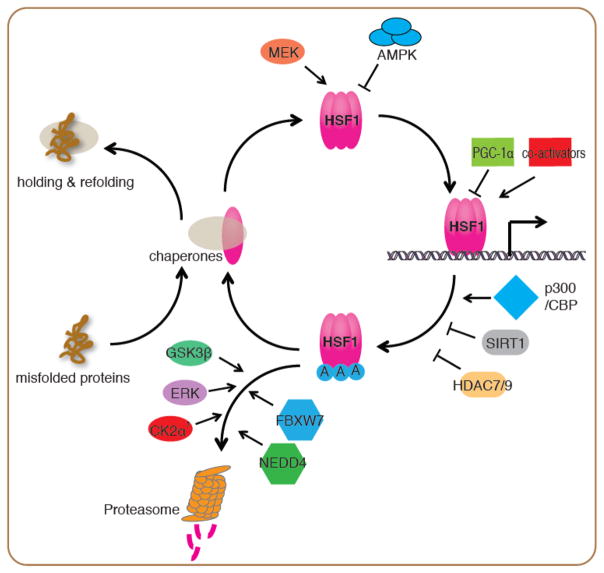
Figure 1.
Regulation of the HSF1 activation and attenuation cycle in the HSR
Upon stress, misfolded proteins dissociate chaperones from HSF1 and allow HSF1 to form DNA-binding competent trimers. MEK promotes HSF1 nuclear translocation and transcriptional activity through phosphorylation at Ser326. Conversely, AMPK inhibits HSF1 nuclear translocation through phosphorylation at Ser121. HSF1 transcriptional activity is regulated by co-activators such as the mediator complex, and repressors including PGC-1α at its target promoters. Attenuation of the HSR is controlled by acetylation of HSF1 at its DNA binding domain by p300/CBP. The histone deacetylases SIRT1, HDAC7 and HDAC9 prevent this acetylation and stabilize HSF1 DNA binding. The E3 ligases FBXW7 and NEDD4 target HSF1 for degradation through the ubiquitin proteasome system, with FBXW7 mediated degradation being promoted by phosphorylation of HSF1 by GSK3β, ERK and CK2 α′ kinases.