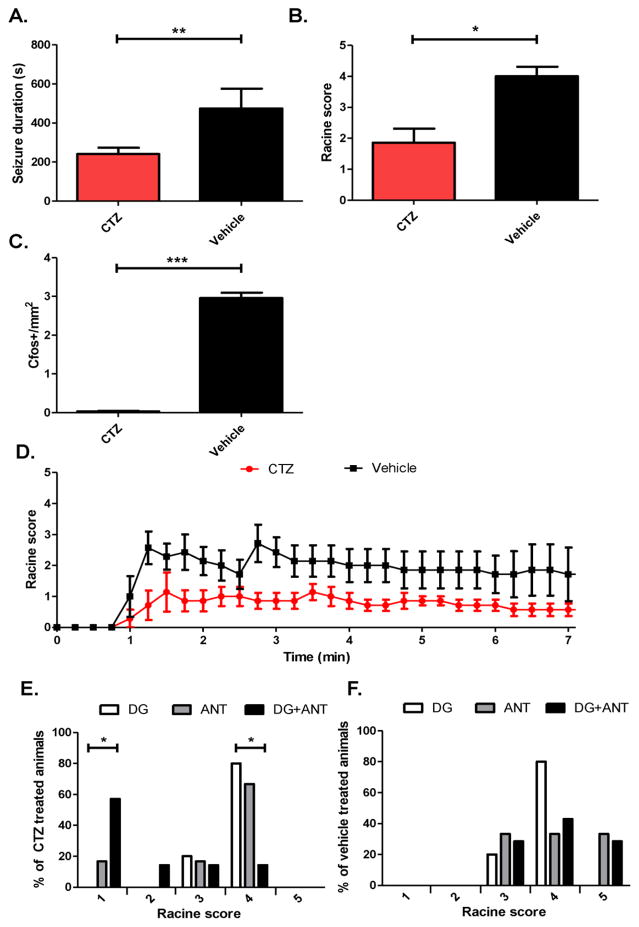
Figure 5. Simultaneous optogenetic inhibition of the DG and ANT reduces overall seizure severity and duration.
CTZ significantly decreased seizure duration (*p<0.01, CTZ group n=5 animals, vehicle group n=4 animals, Student’s t-test) (A), significantly decreased (*p<0.05, n=6 pairs, Wilcoxin matched pairs test) seizure severity (B), and significantly decreased (*p<0.0001, n=19 images for CTZ group, n=16 images for vehicle group, Mann-Whitney test) the amount of c-fos in the DG (C) compared to vehicle. (D) Mean Racine scores over time after PTZ administration. (E) Percentage of CTZ treated animals for each Racine level. There was a significantly higher percentage of animals with Racine level 1 seizures in animals expressing iLMO2 in the DG+ANT compared to DG alone (*p<0.05, n=10 animals for DG group, n=7 animals for DG+ANT group, Fisher’s exact test). In addition, there was a significantly lower percentage of animals with Racine level 4 seizures in animals expressing iLMO2 in the DG+ANT compared to DG alone (*p<0.05, n=10 animals for DG group, n=7 animals for DG+ANT group, Fisher’s exact test). (F) There was no significant difference in the percentage of animals for each Racine level among the different groups that were treated with vehicle. Error bars indicate SEM.