Figure 10.
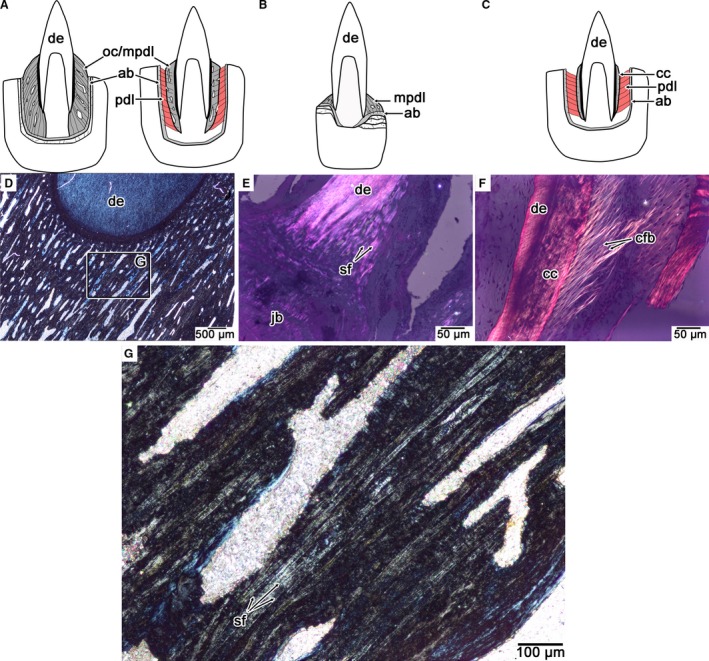
Comparisons of PDL orientation and calcification in mosasaurids, snakes, and crocodilians. (A) Calcified PDL in an ankylosed mosasaurid tooth (thecodont ankylosis), exemplified by Platecarpus (left) and the non‐ankylosed tooth (thecodont gomphosis) of Globidens phosphaticus (right). (B) Calcified PDL in an ankylosed snake tooth (pleurodont ankylosis). (C) Partly calcified PDL in a crocodilian tooth (thecodont gomphosis). (D) Cross‐polarized light image of the calcified PDL in an ankylosed mosasaurid tooth, highlighting the network of calcified PDL fiber bundles (stage and image slightly rotated in order to see the Sharpey's fibers). (E) Cross‐polarized light image of the calcified PDL in the snake Cylindrophis highlighting the network of calcified PDL fiber bundles (stage and image slightly rotated in order to see the Sharpey's fibers). (F) Cross‐polarized light image of the partially calcified PDL of Caiman highlighting the network of non‐calcified PDL fiber bundles. (G) Closeup of the calcified PDL in (A) highlighting the organized network of Sharpey's fibers that form the periodontium in ankylosed mosasaurid teeth. ab, alveolar bone; cc, cellular cementum; cfb, collagen fiber bundle; mpdl, mineralized periodontal ligament; oc, osteocementum; pdl, periodontal ligament; sf, Sharpey's fibers.
