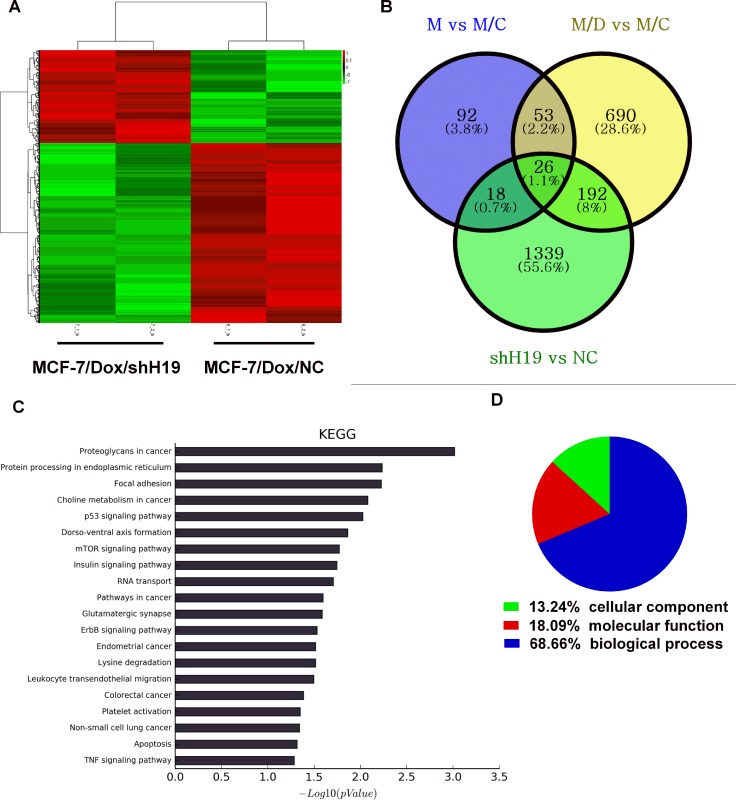
Figure 3. Alternation in H19 lncRNA expression is associated with differential changes in gene expression profiles and signaling pathways in Dox-resistant cells.
Panel A shows a heat map from hierarchical clustering of differentially expressed genes in H19-knockdown MCF-7/Dox/shH19 cells versus the control MCF-7/Dox/NC cells. The red-color represents up-regulated genes and the green color represents the down-regulated genes. Each row represents a single gene. Panel B is a Venn diagram depicting the commonly and differentially expressed genes among control, Dox-resistant and H19-knockdown Dox-resistant cells. After overlapping, a total of 192 genes were identified to be associated with H19-mediated chemoresistance. The blue circle represents the differentially expressed genes between parental MCF-7 (M) and parallel control MCF-7/Con1600 (M/C) cells, the yellow circle represents differentially expressed genes between the Dox-resistant MCF-7/Dox1600 (M/D) and the parallel control M/C, and the green circle represents differentially expressed genes between H19 knockdown MCF-7/Dox/shH19 (shH19) and the control MCF-7/Dox/NC (NC) cells. Panel C shows the KEGG analysis of the top 20 significantly altered pathways upon H19 knockdown in Dox-resistant cells. P values < 0.05 and false discovery rates < 0.05 were used as thresholds to select significant KEGG pathways. The horizontal axis, -log10(pValue), denotes the significance of specific pathways in H19-knockdown MCF7/Dox/H19 cells compared to the corresponding control MCF-7/Dox/NC cells. Panel D shows the GO analysis of the fraction of differentially expressed genes in H19-knockdown MCF7/Dox/shH19 versus the control MCF-7/Dox/NC cells in three GO classifications of cellular component, biological process and molecular function.