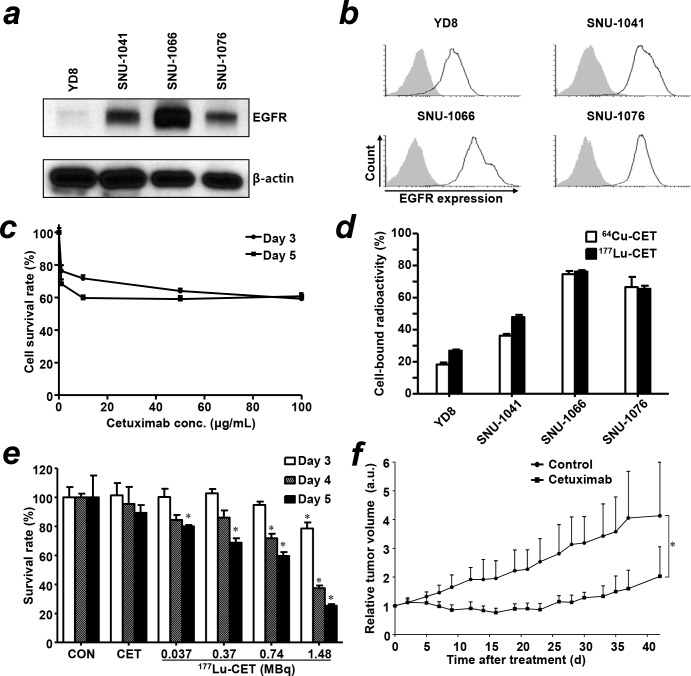
Figure 1. Characterization of EGFR expression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cells, treatment effect of cetuximab and in vitro cell binding assay of radiolabeled cetuximab.
(a) Expression level of EGFR protein in HNSCC cells by western blot. (b) Flow cytometry in HNSCC cells with cetuximab antibody. Gray shaded curve, isotype control; black lined curve, cetuximab. (c) The cytotoxic effect of cetuximab in SNU-1066 HNSCC cells exposed to different concentrations of cetuximab. The viability of SNU1066 cells was evaluated by the MTS assay. (d) In vitro cell binding assay of 64Cu-PCTA-cetuximab (64Cu-CET) and 177Lu-PCTA-cetuximab (177Lu-CET) in HNSCC cells. (e) In vitro therapeutic efficacy of 177Lu-PCTA-cetuximab in SNU-1066 cells. The survival rate (%) of SNU1066 cells was evaluated by Accustain solution (DigitalBio). CON; control, CET; cetuximab. *, vs. control, P < 0.05 (f) Therapeutic efficacy of cetuximab in SNU-1066 HNSCC xenograft model. The relative tumor volumes were measured after injection of saline (control) and six doses of cetuximab (10 mg/kg, thrice per week for 2 weeks). *, vs. control, P <0.05; a.u., arbitrary unit.