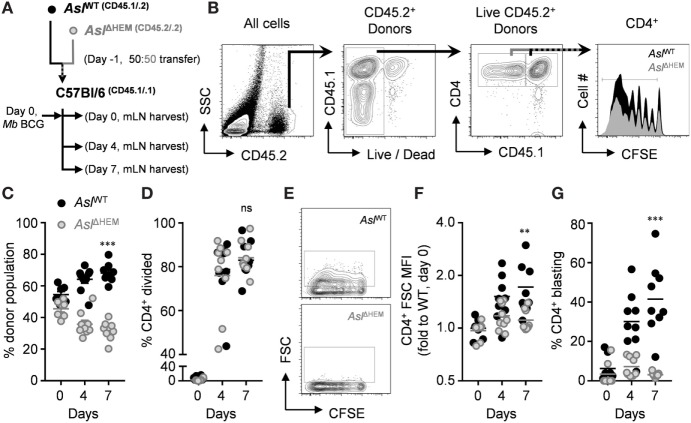
Figure 5.
l-citrulline metabolism drives anti-mycobacterial CD4+ T cell blasting and accumulation in the mLN upon M. bovis BCG infection. (A) CD4+ T cells were collected from P25k;Aslflox/flox;Tie2-cre (AslΔHEM) and P25k;Aslflox/flox;(−) (AslWT) mice and labeled with carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE). Cells were mixed at a 50:50 ratio and transferred i.v. to C57Bl/6 mice (n ≥ 7) one day prior to M. bovis BCG infection (i.n., ~5 × 106 colony forming units). Lung draining mLNs were collected the day after transfer from uninfected mice (day 0), and at 4 and 7 days postinfection. (B) Each donor population and the recipient cells were identified based on congenic CD45 variants, and proliferation of donor T cells was measured by CFSE dilution. Cells were analyzed for ratio of total donor cells (C), proliferation (D), FSC-calculated size (E,F), and blasting frequency [(G), see gated population in (E)]. Data are combined from two experiments. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by two-way AVOVA.