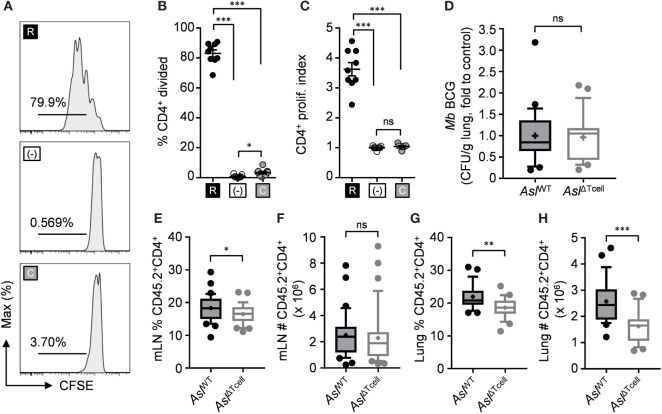
Figure 6.
l-citrulline metabolism is necessary for CD4+ T cell accumulation in the mycobacterial infected lung and mediastinal lymph node in vivo. (A–C) Lymphocytes from Aslflox/flox;CD4-cre (AslΔTcell) were isolated and stained with carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE). Cells were stimulated with α-CD3 in R-free RPMI supplemented with 1 mM l-arginine (black), 1 mM l-citrulline (gray), or neither amino acid added (white) for 72 h. CFSE dilution of CD3+CD4+ T cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. Data are displayed as representative histograms (A), percent of divided cells (B), and by proliferation index (C) as defined in the methods. Data are combined from three experiments. (D–H) Aslflox/flox (AslWT) and AslΔTcell mice were infected with ~5 × 106 colony forming unit M. bovis BCG intranasally. Eight weeks postinfection, mycobacterial burden was quantified in the lungs (D). CD45.2+CD4+ cells were quantified from the mediastinal lymph node (E,F) and infected lung (G,H). Data are combined from three experiments and are displayed as box and whisker plots (n ≥ 22). Error bars, SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by Student’s t-test.