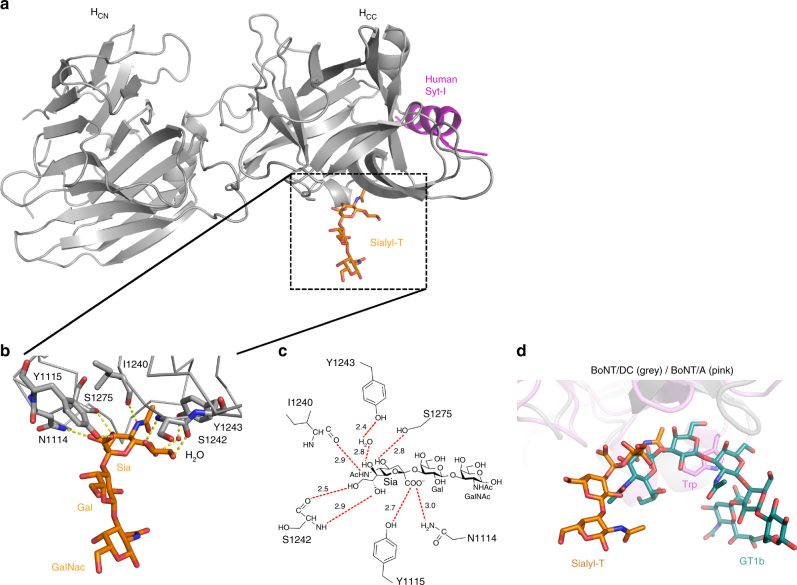
Fig. 4.
Co-crystal structure of BoNT/DC-HC in complex with Sialyl-T. a Overall view of BoNT/DC (gray) with the bound Sialyl-T molecule (orange). Human Syt I (magenta) is modeled in from the previously solved structure of BoNT/DC–Syt I complex (PDB code: 4ISQ). b Close-up view of the Sialyl-T binding site of BoNT/DC, with the protein shown in ribbon, Sialyl-T and the interacting residues as sticks, and one interacting water as a red sphere. Possible hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. c Schematic representation of the possible hydrogen bonds between Sialyl-T and BoNT/DC (red dashed lines). The distance for each bond is shown in Å. d Structural comparison between BoNT/A and BoNT/DC on ganglioside binding. The Sialyl-T binding site in BoNT/DC (shown in gray) is located at a position similar to the GBS in BoNT/A (shown in pink). The sialic acid (Sia) of Sialyl-T (shown in orange) sits in a similar position as the Sia5 group of the GT1b (shown in cyan) bound to BoNT/A. The rest of the Sialyl-T carbohydrates are at a different position than the Gal4-GalNAc3 moieties in GT1b, which form both hydrogen bonds and stacking interactions to a Trp residue in the GBS of BoNT/A