Fig. 7.
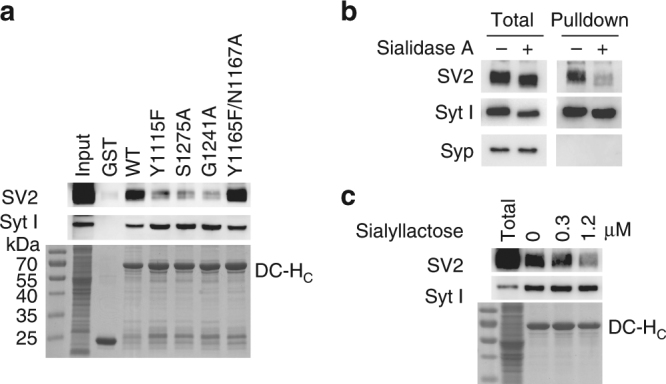
Pulldown of SV2 by BoNT/DC from brain lysates was mediated by binding of the GBS of BoNT/DC to sialic acids in SV2. a GST or GST-fused BoNT/DC-HC were immobilized on beads and incubated with rat brain detergent lysates (in Triton X-100). Pellets were subjected to immunoblot analysis detecting SV2 (upper panel) and Syt I (middle panel), or subjected to Coomassie Blue staining to show GST and GST-fused BoNT/DC-HC proteins (lower panel). WT BoNT/DC-HC pulled down Syt I and SV2. Mutations at the GBS (Y1115F, S1275A, and G1241A) did not affect Syt I pulldown, but reduced SV2 pulldown. Y1165F/N1167A behaved similarly to WT BoNT/DC-HC. b Pull-down assays were carried out using GST-fused BoNT/DC-HC and rat brain detergent extracts pre-treated with sialidase A (0.0125 U per 100 µl lysates for 1 h at 37 °C). Pellets were subjected to immunoblot analysis detecting SV2, Syt I, and Syp. Sialidase treatment cleaves terminal sialic acids from glycosylated proteins, thus reducing the molecular weights of SV2, Syt I, and Syp. Sialidase treatment did not affect Syt I pulldown, but reduced SV2 pulldown. Syp served as a negative control, which did not interact with BoNT/DC-HC. c Pull-down assays were carried out as described in a, with rat brain detergent extracts in the presence of indicated concentrations of sialyllactose. Sialyllactose did not affect Syt I pulldown, but reduced SV2 pulldown in a dose-dependent manner. One of three (a–c) independent experiments is shown
