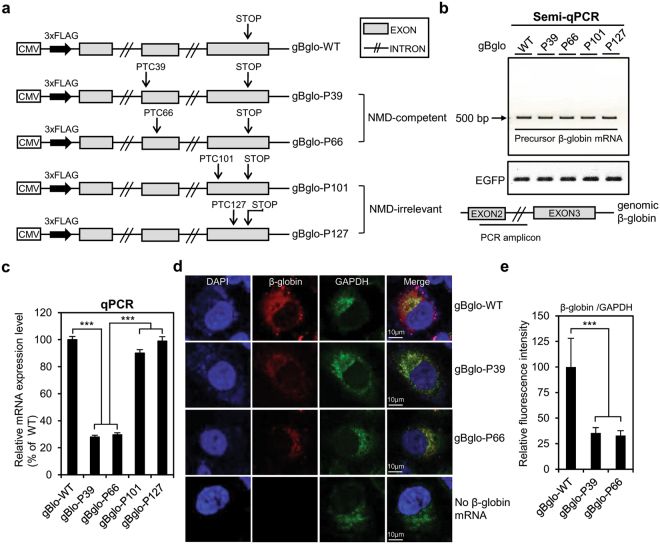
Figure 1.
Construction and expression of vectors containing human genomic β-globin. (a) Schematic diagram of expression vector containing wild-type human genomic β-globin (gBglo-WT) and plasmids derived from gBglo-WT by introducing premature termination codons (PTCs) at the indicated positions. (b) Schematic of location of semi-qPCR amplicon. Semi-qPCR analysis of precursor β-globin mRNA, with EGFP serving as internal control (c) qPCR analysis of mRNA isolated from HeLa cells transfected with the β-globin constructs. (d) RNA-FISH-mediated evaluation of the cytoplasmic localization of β-globin mRNAs from gBglo-WT, gBglo-P39, and gBglo-P66. (e) Immunofluorescence intensity of β-globin was quantified and normalized that of GAPDH mRNA. Every experiment contributing to Fig. 1 was performed three independent times and the results of one representative experiment are shown. One-way ANOVA with a post-hoc test was performed to compare multiple means. ***p < 0.001. Error bars in (c) and (e) represent the SD of the mean of three independently performed qPCR analyses and the SD of the mean of normalized β-globin intensities from 10 randomly selected cells, respectively.