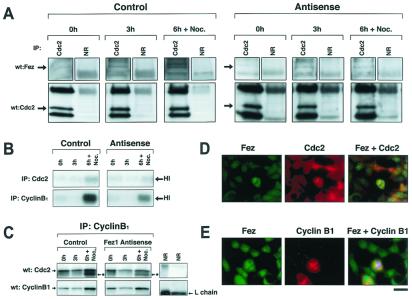
Figure 5.
Association of Fez1 with p34cdc2. (A) Immunoprecipitation of p34cdc2 and Fez1 in synchronized 293 transfectants. 293 cell transfectants expressing antisense FEZ1 vector under control of ecdysone-inducible system were developed to inhibit endogenous Fez1 expression with the ecdysone derivative ponasterone A, as shown in Fig. 4B. 293 antisense FEZ1 transfectants (AS44) were cultured with (Right, Antisense) or without ponasterone A (Left, Control) in medium. 293 transfectants were synchronized by double-thymidine block. After thymidine medium was exchanged, cells were analyzed at 0, 3, or 6 hr plus an additional 2-hr treatment with 40 μg/ml nocodazole (6 h + Noc.). Cellular proteins (1.5 mg) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-p34cdc2 antibody (Cdc2) or normal rabbit serum (NR), followed by immunoblot analysis with anti-Fez1 or with anti-p34cdc2 antibody. (B) Histone H1 phosphorylation after immunoprecipitation with anti-p34cdc2 or with anti-cyclin B1 antibody from synchronized 293 transfectants. Similar to A, samples were subjected to phosphorylation assay with [γ-32P]ATP and histone H1 after immunoprecipitation, separated by SDS/PAGE, and exposed to film. Arrows indicate phosphorylation of histone H1. (C) The p34cdc2 activation in synchronized 293 transfectants. Similar to A, samples were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-p34cdc2 or with anti-cyclin B1 antibody after immunoprecipitation with anti-cyclin B1 antibody. Asterisks with arrows indicate a dephosphorylated active form of p34cdc2. (D and E) Double immunofluorescence with mouse anti-p34cdc2 (D) or mouse anti-cyclin B1 antibody (E), followed by rhodamine-labeled anti-mouse antibody (Middle), or with rabbit anti-Fez1 antibody (D and E), followed by fluorescein-labeled anti-rabbit antibody (Left). Yellow areas depict colocalization of both fluorochromes (Right). Chromatin was stained with Hoechst 2495 to show in blue. (Bar = 10 μm.)