Fig. 5.
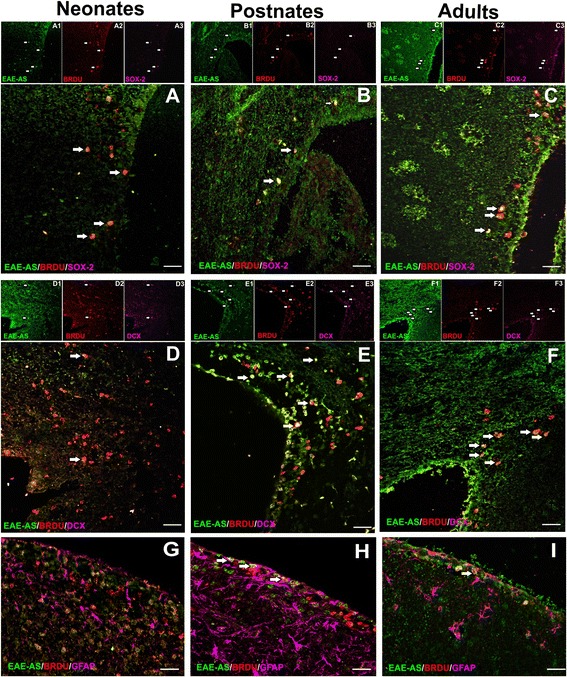
SOX-2, DCX, and GFAP co-labeling with BrdU and EAE-AS in SVZ and periventricular areas. Neonates: SOX-2 (a) colocalizes strongly with EAE-AS+/BrdU+ cells, while DCX (d) co-binding is remarkably less. Postnates: SOX-2 (b) colocalization with EAE-AS+/BrdU+ cells diminishes while DCX (e) escalates, reaching total colocalization with EAE-AS+/BrdU+ cells in adult group (f). SOX-2 co-binding levels at adults (c) are similar to neonate levels. GFAP colocalization levels vary among three age groups. In neonates (g) GFAP is hardly co-labeled with EAE-AS+/BrdU+ cells, whereas in postnates (h), a sharp increase is noted. In adults (i), co-immunostaining is still detected at lower rates. Arrows define triple positive cells and insets above each photo represent signal of each separate marker. Scale bars=30 μm
