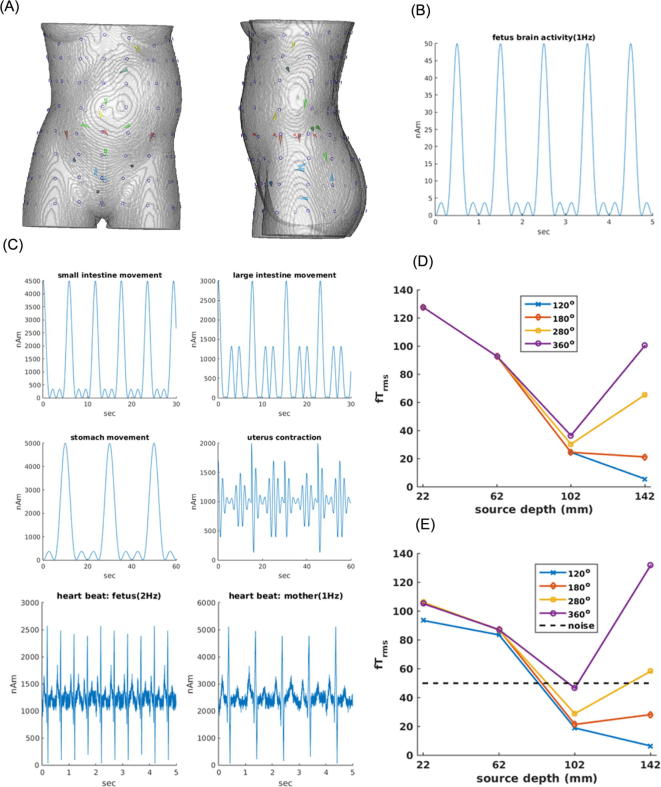
Fig. 9.
Magnetic field rms strength for a current dipole in the fetal brain as a function of the dipole depth and sensor coverage angle with and without interfering magnetic field noise from internal organs. (A) Signal dipole – a single dipole in the fetal brain (red line with a circle) located at 4 positions along the midline close to the axis passing through the navel. Noise dipoles - a single noise dipole located in the maternal and another in the fetal heart (yellow arrows), a single dipole in the maternal stomach (green, just below the maternal heart source), 5 dipoles in the uterus near the cervix (blue arrows), 2 dipoles in the large intestines (brown arrows on the left and right side on the plane of the fetal brain dipole), and 4 dipoles in the small intestines (light green arrows on a posterior plane centered on the fetal brain dipole). (B) Temporal waveform of the fetal brain dipole (50 nAm maximum). (C) Temporal waveforms of the noise dipoles in the internal organs. Note their moments are 2000–6000 nAm, about 100× stronger than the moment of the fetal brain dipole. (D) Maximum rms field strength at the sensor array for the fetal brain dipole located at 4 depths without any noise field from the internal organs. (E) Same with the interfering magnetic field from the internal organs. Dotted line indicates the noise level of the simulated OPM sensors in fTrm. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)