Figure 5.
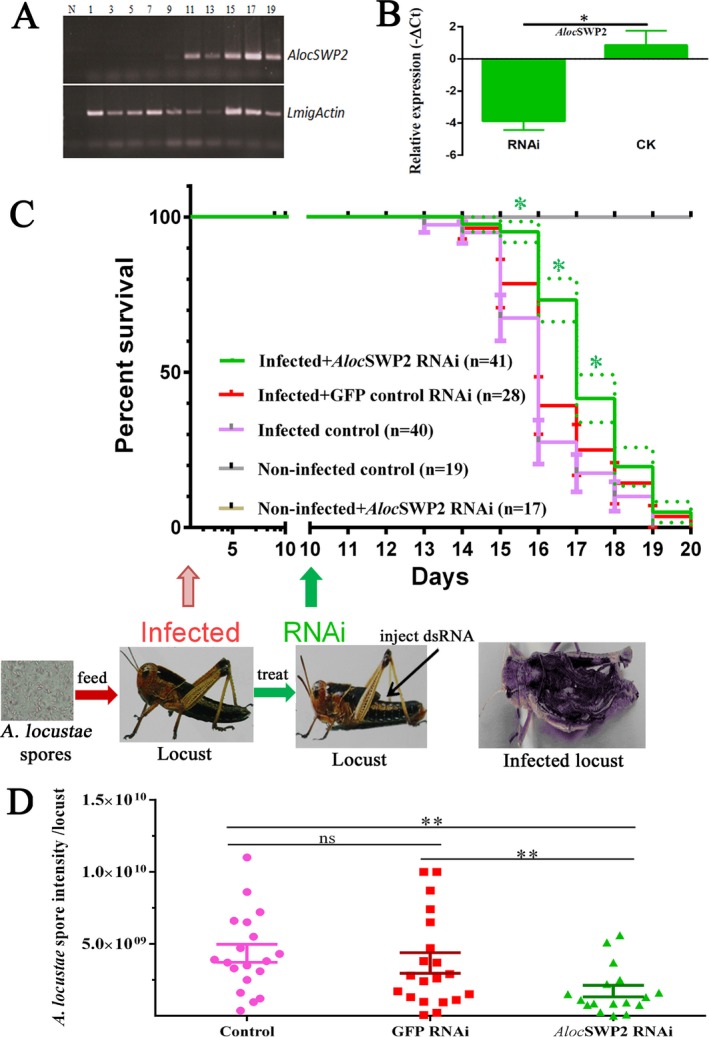
Reduction of the mortality of locusts infected by Antonospora locustae after depression of Aloc SWP2 via RNAi. (A) AlocSWP2 gene expression was detected via RT‐PCR in the fat body of locusts after inoculation. LmigActin is a locust actin gene. Lane: 1, 3, …19 locusts on the days after A. locustae inoculation, N is the negative control. (B) qRT‐PCR experimental result of micro‐injection with dsRNA of AlocSWP2 to interfere with the expression of the gene. Reference gene is A. locustae actin. Bar height denotes the mean average of sample‐specific −ΔCt values, and values are plotted as means ± SEM from at least three repeats. Significant difference at the 0.0016 level. (C) The survivals of locusts inoculated with A. locustae spores or non‐inoculated, and those after treatment with RNAi of AlocSWP2. The 3rd instar nymphs of the locust were infected by A. locustae, then treated with or without RNAi of AlocSWP2. The number (n) of in each group treatment group is noted and three independent repeats of each experiment were done. The arrow indicates the time (days) postinoculation when injection was performed. The Kaplan–Meier method in Graphpad Prism 6 was used to analyze survival data. The t‐test was used for significance analysis, the P value of survival proportions of Infected + Aloc SWP2 RNAi group against Infected + GFP control RNAi group by paired one tail t‐test was 0.0278, which was significantly different. The P value of survival proportions of Infected + Aloc SWP2 RNAi group against Infected control group by paired one tail t‐test was 0.0209, which was significantly different. Bars and dotted line height denote the mean average of SEM. (D) Comparisons of A. locustae spores per locust between the treatments (average spore load). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
