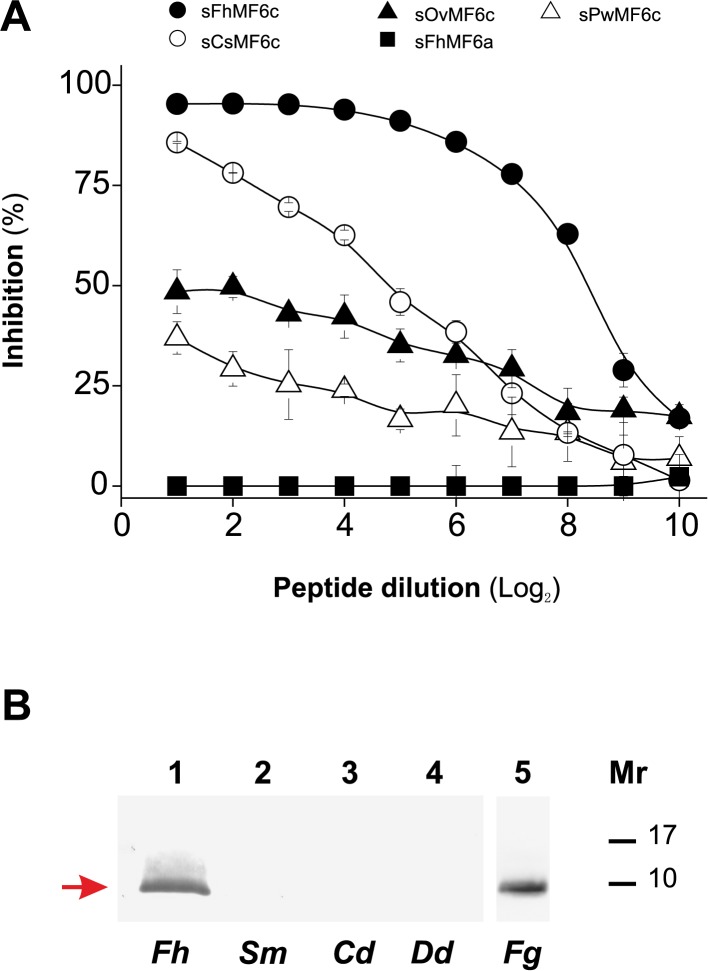
Fig 3. Analysis of the potential cross-reactivity of mAb MF6 with MF6p/FhHDM-1 orthologs from other trematodes.
A) Competitive ELISA with synthetic peptides corresponding to the C-terminal region of MF6p/FhHDM-1 orthologs. ELISA plates coated with sMF6p/FhHDM-1 were incubated with mAb MF6 (diluted 1/200,000) previously incubated with twofold dilutions of sFhMF6c (residues 56A-90N; control for maximal inhibition; filled circles) from F. hepatica, sCsMF6c (residues 56I-89G; unfilled circles) from C. sinensis, sOvMF6c (residues 56I-89K; filled triangles) from O. viverrini, sPwMF6c (residues 56I-89E; unfilled triangles) from P. westermani, and sFhMF6a (residues 23S-55R; filled squares) as a negative control. Data are expressed as percentage inhibition of mAb MF6 by each peptide and are the mean values ± SD of duplicate wells. B) Immunoblotting analysis showing the recognition by mAb MF6 of several natural extracts from different trematodes. Lane 1: Fh (F. hepatica); lane 2: Sm (S. mansoni); lane 3: Cd (C. daubneyi); lane 4: Dd (D. dendriticum); lane 5: Fg (F. gigantica).