Fig 2.
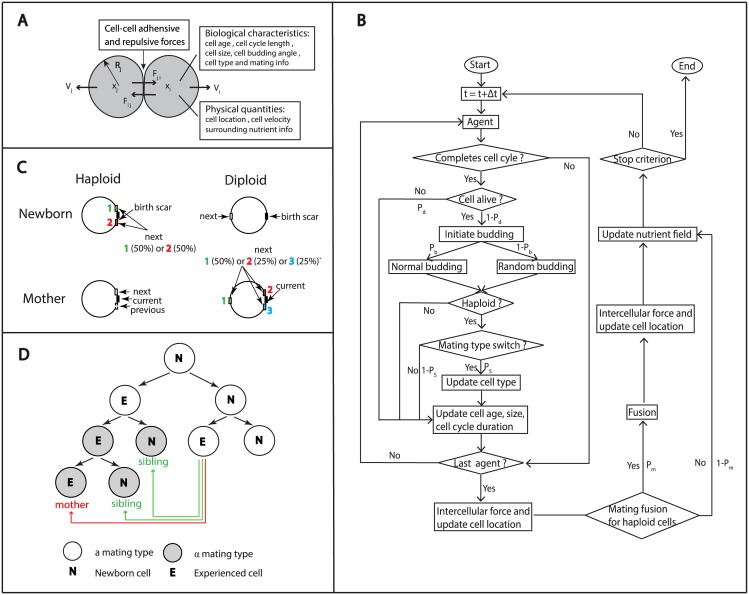
(A) A schematic of the agent-based model, with the key biological and physical quantities. (B) Overview of the processes within a single cell cycle. Pd and Pb are the probabilities of cell death and normal budding (axial for haploid cells and bipolar for diploid cells), respectively. Ps and Pm are the frequencies of mating type switch and successful matings for haploid cells. The simulation stops when the maximal time or the maximal population is attained. (C) Normal budding patterns for haploid and diploid cells. Haploid cells bud in an axial manner: both mother and daughter cells have bud sites adjacent to the previous division site. Diploid cells bud in a bipolar budding pattern: mother cells have a new bud site adjacent to their daughters or on the opposite end of the cell, whereas daughter cells mostly choose a new bud site on the opposite end of the cell. (D) Mating type switch follows certain rules: (1) only experienced cells can switch mating type; (2) mating type switch occurs during the late G1 phase and the switched cells come in pairs; (3) mating type switch occurs at a high frequency. Inbreeding is defined as mating between mother and daughter cells or among siblings.