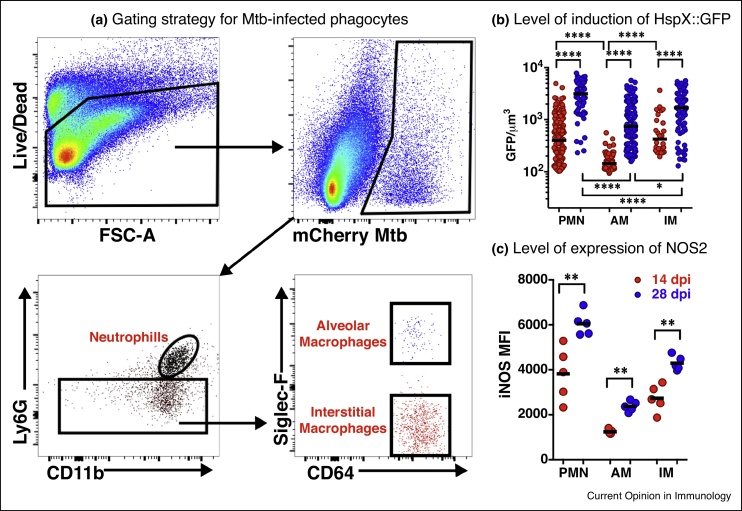
Figure 3.
Examination of the bacterial stress reporter strain hspX’::GFP, smyc’::mCherry Erdman Mycobacterium tuberculosis at the level of different host phagocyte populations in murine lung infection model. (a) The flow cytometry gating strategy for the identification of M. tuberculosis-infected phagocyte subsets from infected mouse lung showing preliminary identification of alveolar macrophages, interstitial macrophages, and neutrophils. (b) The level of expression of NO-driven GFP under regulation of the hspX promoter identifying those phagocytes that induce the highest level of bacterial stress, and how the stress intensifies from 14 to 28 days post-infection. The levels of induction of expression of GFP indicate that the most stressful host cells appear to be neutrophils, and the least stressful, alveolar macrophages. (c) Labeling of the host cells with antibody against NOS2 demonstrates the direct correlation between expression levels of the host nitric oxide synthase, NOS2, and levels of expression of the bacterial stress response reporter hspX’::GFP (B).