Fig. 7. Proposed pathway whereby Fabp1 and Scp-2/Scp-x gene products facilitate hepatic phytol metabolism.
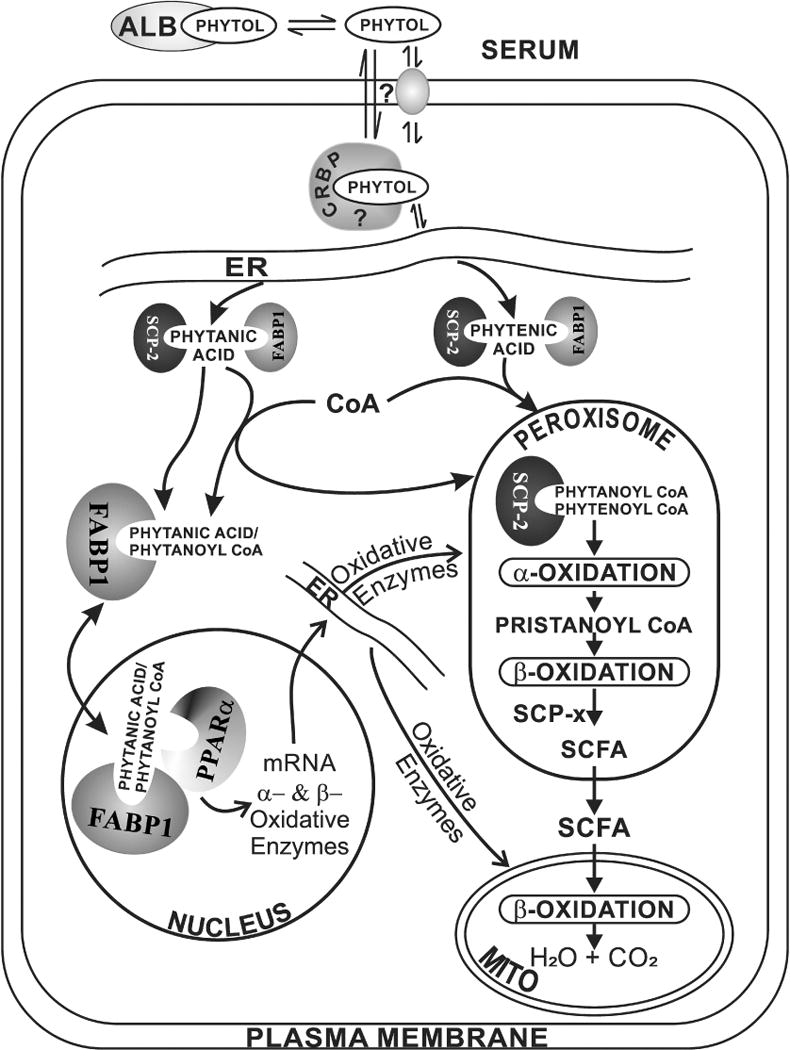
In serum, phytol is bound to albumin [64]. Phytol dissociates from albumin-phytol complexes for uptake across the hepatocyte plasma membrane (PM) by as yet unknown mechanism(s) (e.g. diffusional, carrier mediated). While it is not known how the poorly aqueous-soluble phytol traffics to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), it is not mediated by FABP1 or SCP-2 since neither binds phytol. Nevertheless, due to its insolubility a carrier protein is likely required, potentially cellular retinol binding protein (CRBP) or another cytosolic carrier protein. At the ER, phytol is metabolized to phytanic acid and phytenic acid—both of which are bound by FABP1 (the most prevalent lipidic carrier/chaperone protein in liver, highly localized in cytosol [65, 66]) as well as SCP-2 (several fold less present than FABP1 in liver, equally distributed between cytosol and peroxisomes [9–11]). FABP1 and SCP-2 then transport bound phytanic acid and phytenic acid to the peroxisomal membrane for conversion to/internalization of their respective CoA thioesters. Peroxisomally localized SCP-2 [9–11] then binds phytanoyl-CoA and phytenoyl-CoA [5, 6]. It is important to note that, with some exception [67], there is little evidence for FABP1 localization within peroxisomes [65, 66]. Within the peroxisomal matrix SCP-2 then facilitates peroxisomal oxidation of phytanoyl-CoA and phytenoyl-CoA by directly interacting with and transporting the bound ligands to oxidative enzymes. For example, in vitro studies show that SCP-2 stimulates peroxisomal phytanoyl-CoA 2-hydroxylase which is the key enzyme and first step in peroxisomal α-oxidation of branched-chain fatty acids [7, 12]. Downstream of this step, the other Scp-2/Scp-x gene product (i.e. SCP-x, exclusively peroxisomal) is the only known branched-chain 3-ketoacyl CoA thiolase [4, 9, 60, 68]. Several cycles of α- and β-oxidation then successively shorten the branched-chain fatty acids to short chain fatty acids (SCFA) less than 12 carbons long. SCFAs are not bound by either SCP-2 [5, 23] or FABP1 [69–72], but instead readily diffuse across the peroxisomal membrane into the cytosol and subsequently across the mitochondrial membranes for completion of β-oxidation within the mitochondrial matrix.
