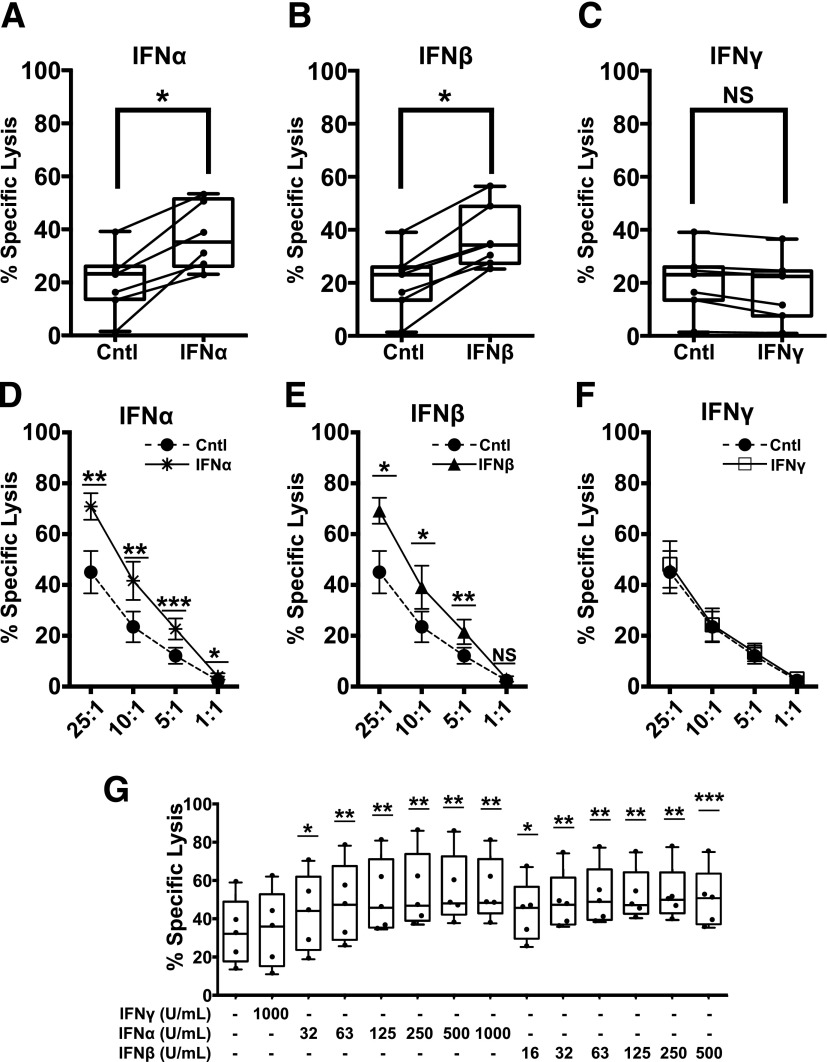
Figure 1.
Short-term exposure of autoreactive CTLs to T1-IFNs enhances cytotoxicity toward β-cells. IGRP-CTL avatars were exposed to IFNα, IFNβ, or IFNγ for 2 h. Cytokines were removed by washing, and then IGRP-CTL avatars were cocultured with dispersed primary human islets (A–C) or βL5 (D–F) for 16 h in a standard CML. A–C: Box-and-whisker plots represent the percentage of dispersed human islets lysed by IGRP-CTL avatars. Data for the interferon-mediated change in effector function for each individual T-cell donor is provided using a scatter plot with connecting lines. D–F: Lines represent the percentage of specific lysis induced by IGRP-CTL avatars primed with IFNα (1,000 units/mL) (A and D), IFNβ (500 units/mL) (B and E), or IFNγ (1,000 units/mL) (C and F) over several E:T ratios. G: IGRP-CTL avatars were primed with various concentrations of T1-IFN for 2 h and cocultured with βL5 at a 10:1 E:T for 16 h in CML. Data are plotted as mean ± SEM, where T cells from each donor (7 donors for A–C, 6 donors for D–F, and 5 donors for G) were weighted equally. There were at least three separate experiments for each donor. Statistical significance was assessed using a nonparametric paired t test with Wilcoxon post-test analysis. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.