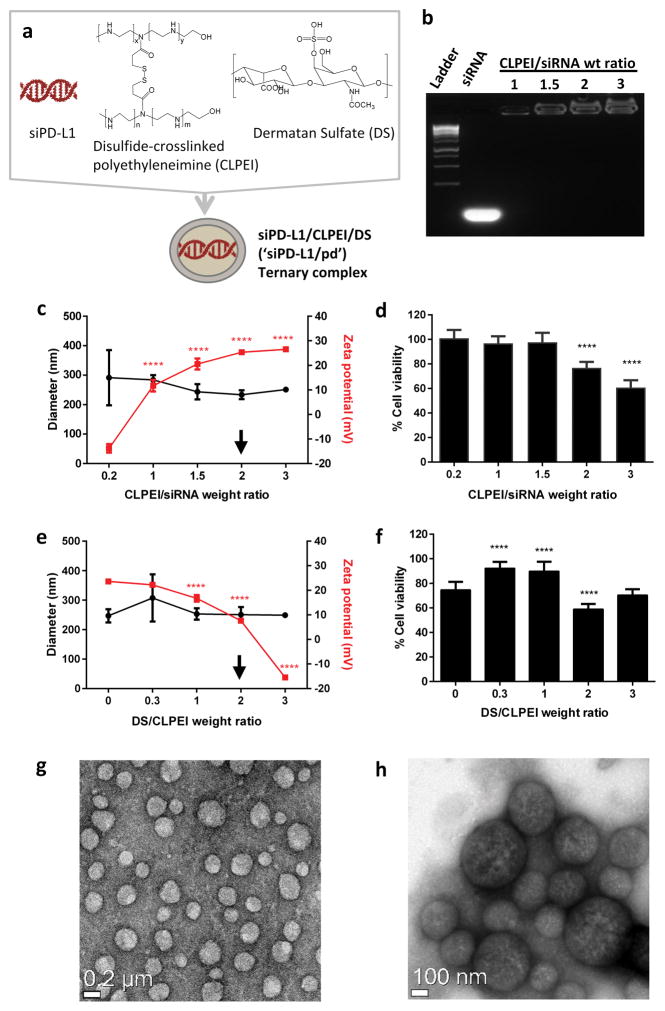
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of siPD-L1/CLPEI/DS (‘siPD-L1/pd’) ternary complex. (b) Formation of siRNA-CLPEI binary complexes, confirmed by electrophoresis. (c) Hydrodynamic diameters (circle) and zeta potentials (square) of siRNA-CLPEI binary complexes with different CLPEI/siRNA ratios. n = 3 identically prepared samples, mean ± s.d. (d) Viability of B16F10 cells after 6 h incubation with binary complexes and additional incubation for 42 h in treatment-free medium. n = 3 identically prepared samples, mean ± s.d. ****: p < 0.0001 vs. CLPEI/siRNA ratio of 0.2 by Dunnett’s test. (e) Hydrodynamic diameters (circle) and zeta potentials (square) of siRNA-CLPEI-DS ternary complexes with different DS/CLPEI ratios (CLPEI/siRNA ratio fixed at 2). n = 3 identically prepared samples, mean ± s.d. (f) Viability of B16F10 cells after 6 h incubation with ternary complexes and additional incubation for 42 h in treatment-free medium. n = 3 identically prepared samples, mean ± s.d. ****: p < 0.0001 vs. DS/CLPEI ratio of 0 by Dunnett’s test. (g–h) TEM images of siPD-L1/pd complex. Low magnification (g) and high magnification (h).