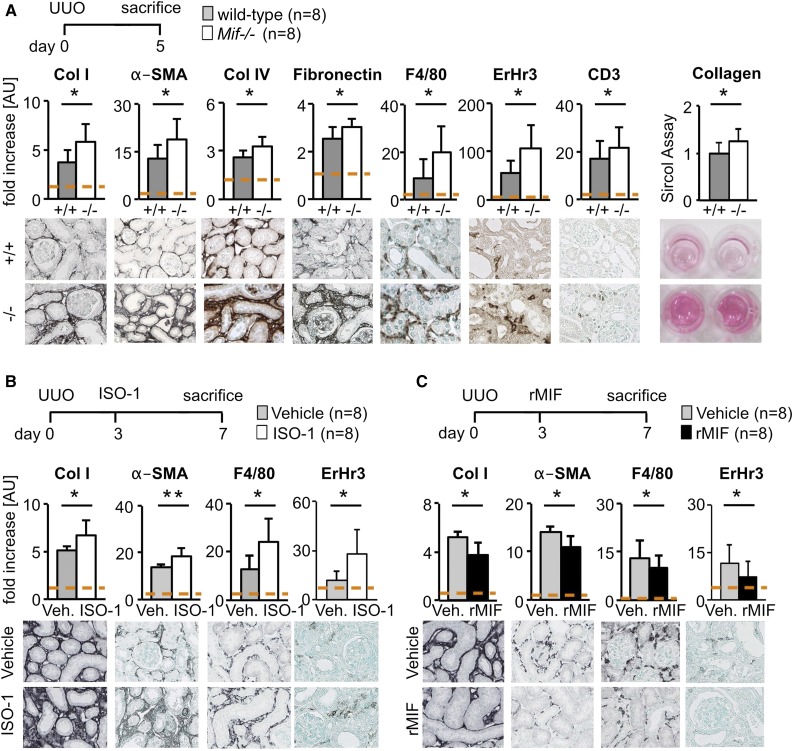
Figure 1.
MIF was antifibrotic in obstructive nephropathy. (A) In a model of renal fibrosis, the UUO on day 5, compared with wild-type littermates (+/+), Mif deficient (−/−) mice had significantly increased renal fibrosis and inflammation as shown by computer-assisted morphometry of sections stained for fibrosis markers, i.e., collagen type I (Col I), collagen IV (Col IV), fibronectin, and α-SMA, and markers of inflammatory infiltrates, i.e., macrophages and monocytes (ErHr3 and F4/80) and T-cells (CD3). Biochemical assay for collagen content (Sircol) confirmed these results. (B) Compared with vehicle-treated mice, MIF neutralization with a specific small-molecule inhibitor, ISO-1 (40 mg/kg body wt daily i.p.), initiated in established disease on day 3 of UUO also significantly increased accumulation of myofibroblasts, collagen deposition, and immune cell infiltration compared with vehicle-treated (Veh.) mice. (C) Vice versa, compared with vehicle-treated mice, treatment with murine rMIF (2 mg/kg body wt daily i.p.) in established fibrosis in UUO decreased renal fibrosis and inflammation. Data are mean±SD; n=8 per group in all experiments. Values of healthy contralateral kidneys of WT were set as 1, represented by the dashed line. *P<0.05; **P<0.01. AU, arbitrary unit.