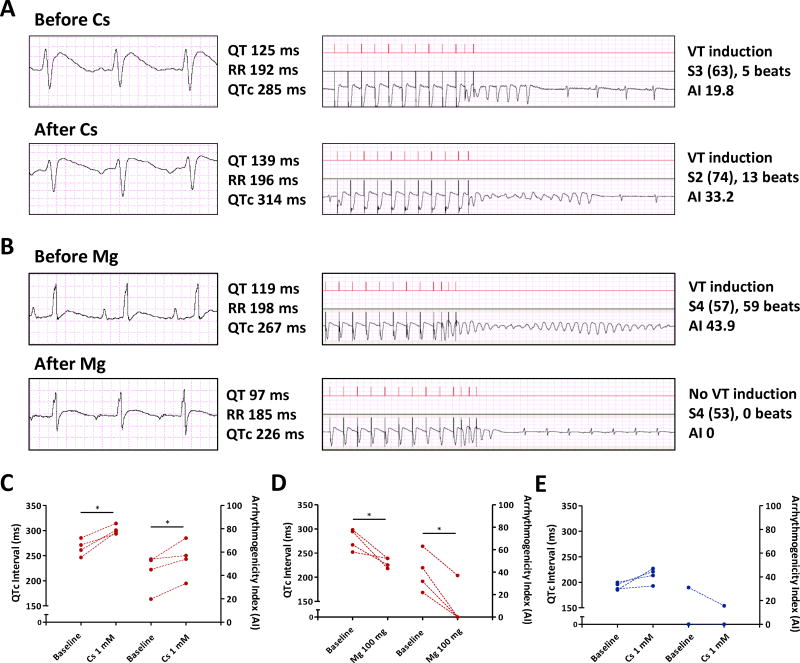
Figure 4. Reduced repolarization reserve in HFpEF rats.
A. 10 ml of 1 mM cesium chloride delivered through tail vein in a HFpEF rat prolonged QTc from 285 ms to 314 ms and worsened arrhythmia (AI from 19.8 to 33.2). B. 100 mg of magnesium sulfate delivered intravenously in a HFpEF rat decreased QTc interval from 267 ms to 226 ms and abolished the arrhythmia (AI 43.9 to 0). C. Cesium chloride prolonged QTc in HFpEF rats (left Y axis) and worsened VA (AI in right Y axis). HFpEF rats n=4. D. Magnesium sulfate shortened QTc interval in HFpEF rats (left Y axis) and decreased AI (right Y axis). HFpEF rats n=4. E. Cesium chloride in control rats prolonged QTc interval (left Y axis) but failed to induce VA (AI in right Y axis). Control rats n=4. * denotes p < 0.05. Paired t-test was used for 4C-E.