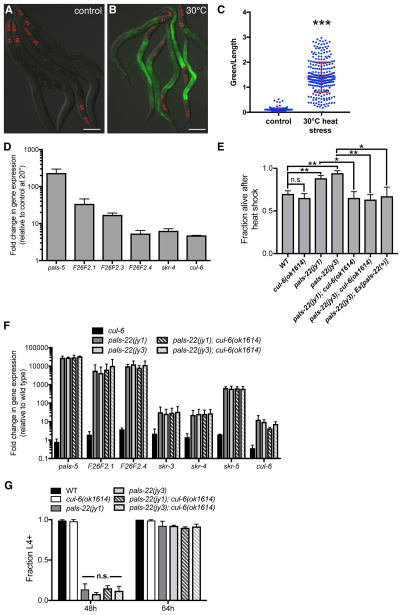
Figure 2. IPR gene expression is increased by heat stress, and pals-22 mutants have increased survival after heat shock, dependent on the cullin cul-6.
(A,B) pals-5p::GFP animals grown at (A) 20°C or (B) shifted to 30°C for 24h. Green is pals-5p::GFP, red is myo-2p::mCherry expression in the pharynx as a marker for presence of the transgene. Images are overlays of green, red and Nomarski channels and were taken with the same camera exposure for all. Scale bar, 100 μm. (C) pals-5p::GFP expression quantified in pals-22 mutants using a COPAS Biosort to measure the mean GFP signal and length of individual animals, indicated by blue dots. Mean signal of the population is indicated by red bars, with error bars as SD. Graph is a compilation of three replicates, with at least 100 animals analyzed in each replicate. *** p < 0.001 with Student’s t-test. (D) qRT-PCR measurement of gene expression in wild-type animals shifted to 30°C for 24h, shown as the fold change relative to wild-type worms grown at 20°C. Results shown are the average of two independent biological replicates, error bars are SD. (E) pals-22 mutants have increased survival after heat shock, which is suppressed by a cul-6(ok1614) deletion. Animals were treated for 2h at 37°C followed by 24 hours at 20°C, and then assessed for survival. Strains were tested in triplicate, with at least 30 animals per plate. Mean fraction alive indicates the average survival among the triplicates, errors bars are SD. ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05, n.s., not significant with Student’s t-test. Assay was repeated three independent times with similar results, and data from a representative experiment are shown. (F) qRT-PCR measurement of IPR gene expression, shown as the fold change relative to wild-type control. Results shown are the average of two independent biological replicates, error bars are SD. (G) pals-22 mutants have a developmental delay, which is not suppressed by cul-6(ok1614) deletion. Percentage of animals reaching the L4 larval stage at timepoints after eggs were laid is indicated. Results shown are the average of three independent biological replicates, with 100 animals assayed in each replicate. Error bars are SD. n.s., not significant with Student’s t-test. Related to Figures S2 and S3.