Fig. 2. Mn exposure reduced mitochondrial mass and induced mitochondrial dysfunction in astrocyte cell cultures.
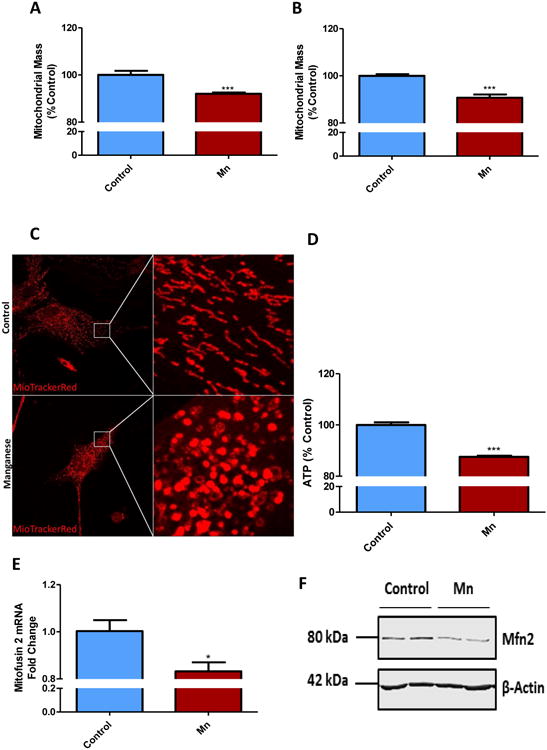
100 μM Mn for 24 h induced loss in mitochondrial mass in primary mouse astrocytes (A) and in U373 cell line (B), as shown by MitoTracker green assay. (C) 100 μM Mn exposure shifted mitochondrial morphology in primary astrocytes, as shown by MitoTracker Red. (D) CellTiter Glo assay reveals Mn reduced ATP production in primary astrocytes. (E) q-RT-PCR and (F) Western blot analyses show 100 μM Mn exposure for 24 h reduced Mitofusin2 (Mfn2) in primary mouse astrocytes. Data analyzed via Student's t test, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Data represented as mean±SEM with 3-8 biological replicates from 2-3 independent experiments.
