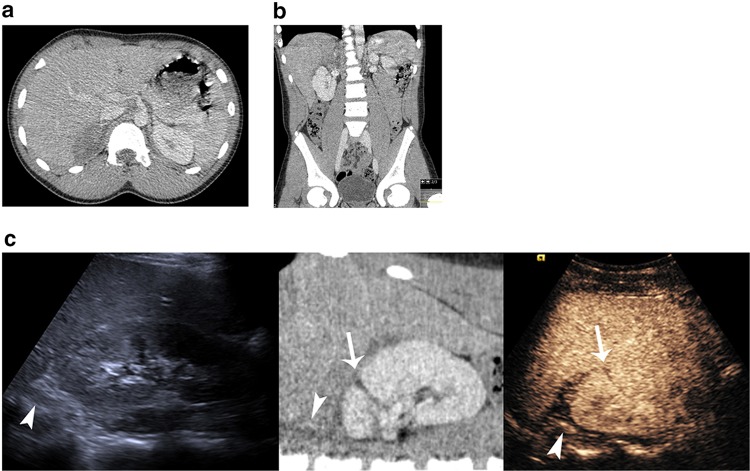
Fig. 1.
A 13-year-old boy with renal laceration and adrenal hematoma. Axial CT image a demonstrates a rounded hypodense lesion displacing the right adrenal gland. Coronal reformatted image b demonstrates the relation of the hematoma to the right kidney, liver and adrenal gland. A composite image c correlating US (left), CT (middle) and CEUS (right). The adrenal gland (arrowheads) can be seen hypoechoic with US and normally enhancing with CT and CEUS. The hematoma is identified surrounding the adrenal gland. It is readily identified on CT as hypodense material and is more prominent on CEUS where it is avascular distinct to adjacent normal enhancing tissues. The kidney laceration (arrow) is visible on CT and CEUS but less prominent on US