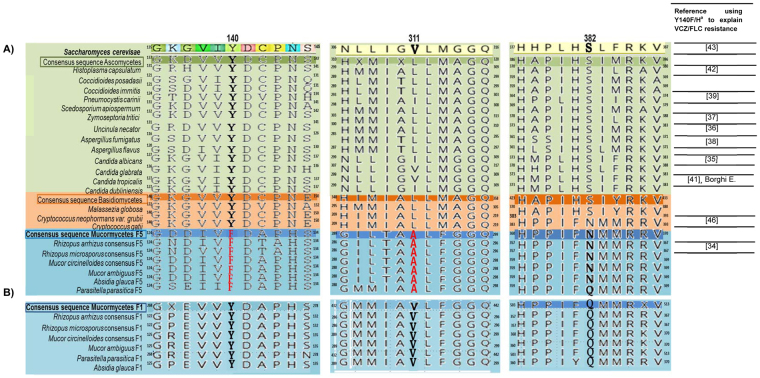
Figure 2.
Amino acid sequence alignment of lanosterol 14-α demethylase in human pathogenic fungi. Proteins belonging to sixteen fungi with consensus sequences of six Mucorales CYP51s. (A) Alignment using Saccharomyces cerevisiae Erg11 as reference (partial amino acid sequence colored) compared with wild-type ascomycete strains (n = 13) (in light green) with phylum consensus (dark green); wild-type basidiomycetes (n = 3) (light orange) with phylum consensus sequence (dark orange); sequences of R. arrhizus (n = 3), R. microsporus (n = 13), and M. circinelloides (n = 18) CYP51 F5 sequences, together with Mucor ambiguus, Parasitella parasitica, and Absidia glauca LDM sequences (light blue), with subphylum consensus sequence (dark blue). The frequently mutated tyrosine residue homologous to S. cerevisiae CYP51 Y140 is marked in bold, and the change to phenylalanine is seen in all our CYP51 F5 Mucorales species (original position F129) shown in red. The V to A substitution in position 311 (S. cerevisiae numbering) is only observed among Mucorales LDM F5 sequences, and are depicted in red. The Q/N side chains aligning with S. cerevisiae LDM S382 are marked in bold. Superscript numbers show the positions of the 5′ and 3′ amino acids for each sequence. The last column gives references reporting a mutation homologous to Y140F/H as responsible for short-tailed azole resistance in the species indicated; aaccording to S. cerevisiae numbering. (B) Shows the same alignment with consensus sequences of six Mucorales CYP51 F1s. The residue homologous to ScErg11p Y140 is marked in bold and is seen also in the protein sequence of the six Mucorales CYP51 F1s. In position 311 (S. cerevisiae numbering), a V is also present in all Mucorales CYP51 F1s. The Q/N side chains are also present in Mucorales CYP51 F1, marked in bold, and in both LDMs do not affect VCZ binding.