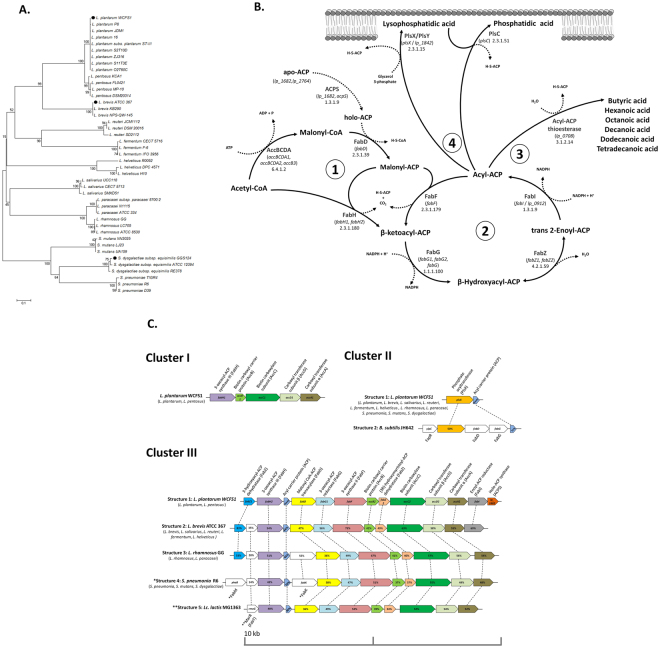
Figure 2.
(A) Unrooted Neighbour-Joining tree based on the amino acid sequences of 43 acyl-ACP thioesterases (TEs) present in 13 gram positive bacterial species. TEs demonstrated capable to produce butyric acid are marked with black dots30. (B) Schematic representation of the conserved type II fatty acid biosynthesis pathway (FASII) and phosphate acyltransferase system (Pls) in L. plantarum species based on the reference strain L. plantarum WCFS1. Briefly, in the FASII initiation (1) the four separated subunits of acetyl-CoA carboxylase enzyme (Acc) catalyze the formation of malonyl-CoA starting from acetyl-CoA, with the biotin as covalently attached cofactor. Subsequently, the transacylase FabD substitutes the CoA for an acyl carrier protein (ACP), which is previously activated by phosphopantetheinyl-transferase (ACPS). The malonyl-ACP is condensed by FabH to acetyl-CoA, forming the β-ketoacyl-ACP. The β-ketoacyl-ACP enters in the iterative process of fatty acids chain-elongation (2), in which it is reduced by the FabG enzyme and dehydrated, first by FabZ (reversible reaction) and then by FabI (else FabK), producing the first four-carbons chain (C4) acyl-ACP. From this point the elongation process can continue through the dehydration of acyl-ACP carried out by FabF, or may be interrupted by a (3) medium-chain ACP-thioesterase (WP_003645113.), which cleaves the ester bonds and release free fatty acids with a chain length ranging from C4 and C1430. Once elongated up to C1482 the acyl-ACPs are transferred to the cells membrane (4) by acyltransferase (PlsX, PlsY, PlsC). (C) Genetic maps of FASII-Pls related genes in L. plantarum WCFS1 (representative loci organization of L. plantarum and L. pentosus species) and comparison with other Gram positive bacteria loci organizations, represented by the reference strains: L. brevis ATCC 367, L. rhamnosus GG, S. pneumoniae R6, Lc. lactis MG 1363 and B. subtilis JH 642. Species that have the same loci organization of each reference strain are reported in parentheses. Orthologous genes are denoted by the same color and connected by dashed lines while genes not present in L. plantarum are blanks. Proteins encoded are reported above or below the gene locus and the percentage of the amino acids similarity is reported for each homologous protein compared to L. plantarum WCFS1, or otherwise compared to a reference strain marked with asterisks (*).