Fig. 8.
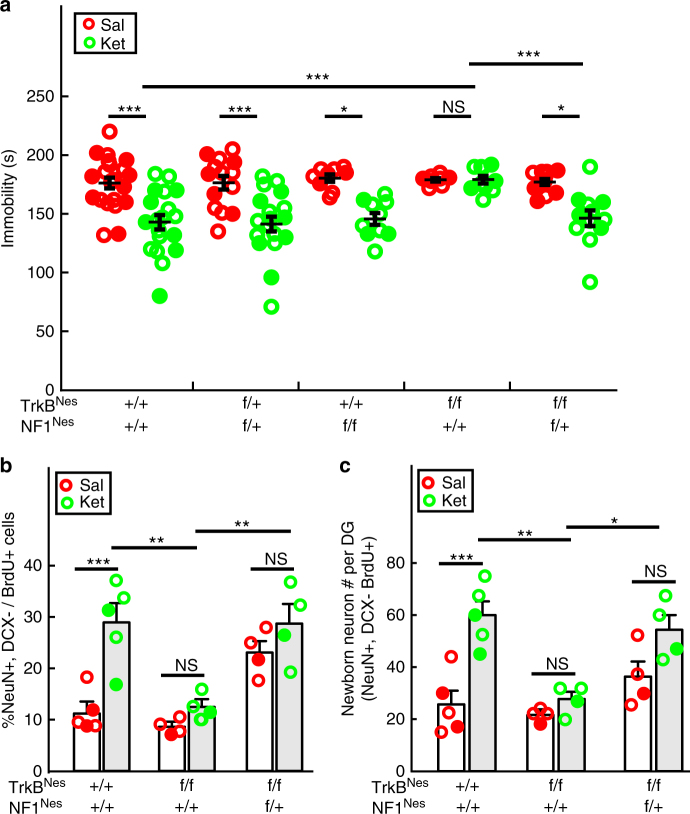
NF1 ablation rescues both neurogenic and behavioral deficits in mice with lacking TrkB in NPCs. a Ketamine significantly decreased immobility time in the FST in control, NF1Nes/TrkBNes double heterozygotes and NF1Nes mice, but not in TrkBNes mice. NF1Nes heterozygous (f/+); TrkBNes double-mutant mice reversed the impaired response to ketamine, as displayed by a significant reduction of immobility time in the FST (two-way ANOVA with unweighted mean analysis, Tukey post hoc, ***p = 1.664E−5 for ketamine-treated TrkBNes vs control mice; ***p = 3.15E−4 for ketamine-treated TrkBNes vs TrkBNes; Nf1Nes f/+; other comparisons were made between saline and ketamine within each genotype group). b Percentage of newborn neurons in ketamine-treated TrkBNes mice was significantly decreased compared to ketamine-treated control mice. In contrast, TrkBNes; NF1Nes f/+ mice displayed enhanced mature neuron generation compared to TrkBNes mice (two-way ANOVA, Tukey post hoc, ***p = 0.0001 for saline vs ketamine in control mice; **p < 0.01 for ketamine-treated TrkBNes vs control (p = 0.0012), or vs TrkBNes; NF1Nes f/+ mice (p = 0.0081); not significant for saline vs ketamine in TrkBNes mice (p = 0.8555) and TrkBNes; NF1Nes f/+ mice (p = 0.6792)). c Production of newborn neurons was rescued in ketamine-treated TrkBNes; NF1Nes f/+ mice compared to TrkBNes mice (two-way ANOVA, Tukey post hoc, ***p = 0.0004 for saline vs ketamine in control mice; **p = 0.0014 for ketamine-treated TrkBNes vs control, *p = 0.0145 for ketamine-treated TrkBNes vs TrkBNes; NF1Nes f+ mice; not significant for saline vs ketamine in TrkBNes mice (p = 0.9749) and saline vs ketamine in TrkBNes; NF1Nes f/+ mice (p = 0.1674)). Circles in solid color denote the data points from female mice