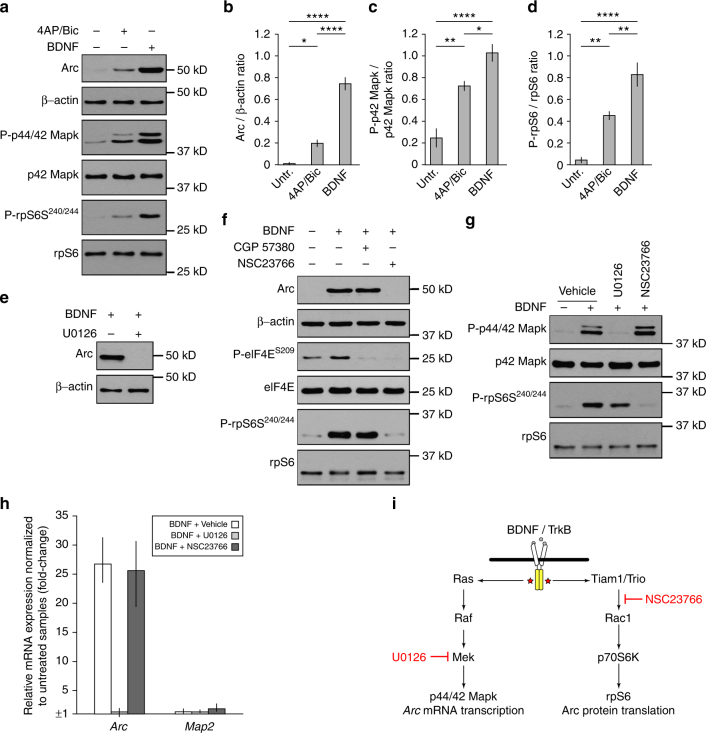
Fig. 1.
Profiling of signaling pathways supporting BDNF-induced Arc expression in mouse primary cortical neurons. a Western blots showing levels of Arc, phospho-p44/42 Mapk, and phospho-rpS6 in DIV13 primary cortical neurons that were treated for 6 h with a 4AP (40 µM) + Bic (50 µM) cocktail or BDNF (100 ng ml−1). Untreated cells were included as control. b–d Graphs show mean (n = 4) Arc/β-actin (b), phospho-p42 Mapk/p42 Mapk (c), or phospho-rpS6/rpS6 (d) (±SEM) ratios for cells treated as in a. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) revealed a significant difference between treatment for each antigen (Arc, F 2,9 = 101.52, p < 0.0001; phospho-p42 Mapk, F 2,9 = 31.74, p < 0.0001; phospho-S6, F 2,9 = 34.49, p < 0.0001). Tukey’s HSD post hoc test, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001. e Western blot of Arc protein expression in cortical neurons co-treated for 6 h with BDNF plus vehicle (DMSO) or Mek/Mapk pathway inhibitor U0126 (10 µM). f Similar experiment as in e was conducted with Mnk1 inhibitor CGP 57380 (5 µM) or Rac1 inhibitor NSC23766 (200 µM). Experiments in e, f were done in duplicate and lysates were probed for phospho-eIF4E, phospho-rpS6, and/or phospho-p44/42 Mapk (g) as control. h Arc mRNA expression in cortical neurons treated for 6 h with BDNF plus vehicle, U0126, or NSC23766. Inhibition of Mek/Mapk pathway by U0126 prevented BDNF-induced Arc expression but not Rac1 inhibition by NSC23766. Map2 expression was assessed as control. Bars represent mean fold-change measured by RT-qPCR (error bars indicate range from three biological replicates). i Schema summarizing the contribution of Mek/Mapk and Rac1/rpS6 signaling to BDNF-induced Arc expression in primary cortical neurons