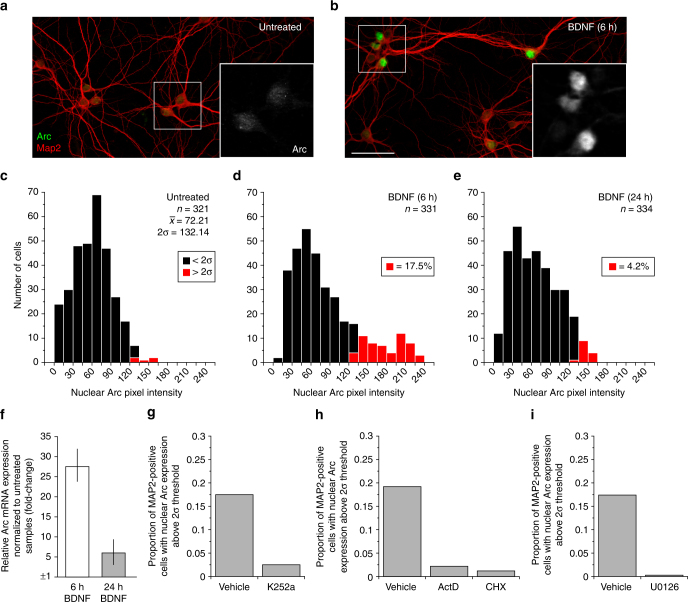
Fig. 2.
Validation of a high-content image-based nuclear Arc assay adapted for high-throughput chemical screening. a, b Representative immunostaining of Arc (green fluorophore) in untreated DIV14 mouse primary cortical neurons (a) and cells that were treated with BDNF for 6 h (b). Cells were co-immunostained with the neuronal marker Map2 (red fluorophore) to confirm specificity of staining to neurons. The high-magnification bottom-right insets in each panel show that Arc immunostaining in a BDNF-treated culture is particularly abundant in the nuclear compartment at this time point. Scale bar 50 µm. c–e Quantification of a set of biological replicates (triplicates) reveal that 17.5% of neurons (Map2-positive cells) have above threshold nuclear Arc expression (equal to or above 2σ of average nuclear Arc pixel intensity) 6 h after application of exogenous BDNF but only 4.2% after 24 h. f Quantitative real-time PCR Arc mRNA analysis shows a consistent difference as in d, e between cortical neurons treated for 6 and 24 h. Bars represent mean fold-change measured by RT-qPCR (error bars indicate range from three biological replicates). g–i BDNF-induced nuclear Arc protein expression is blocked by the co-application of a pan-inhibitor of receptor tyrosine kinases (k252a, 100 nM), RNA transcription (actinomysin D (ActD), 2 ng ml−1), protein biosynthesis (cycloheximide (CHX), 50 µg ml−1), or Mek/Mapk signaling (U0126, 10 µM), demonstrating that this assay can be adapted to perform a large-scale, image-based screening