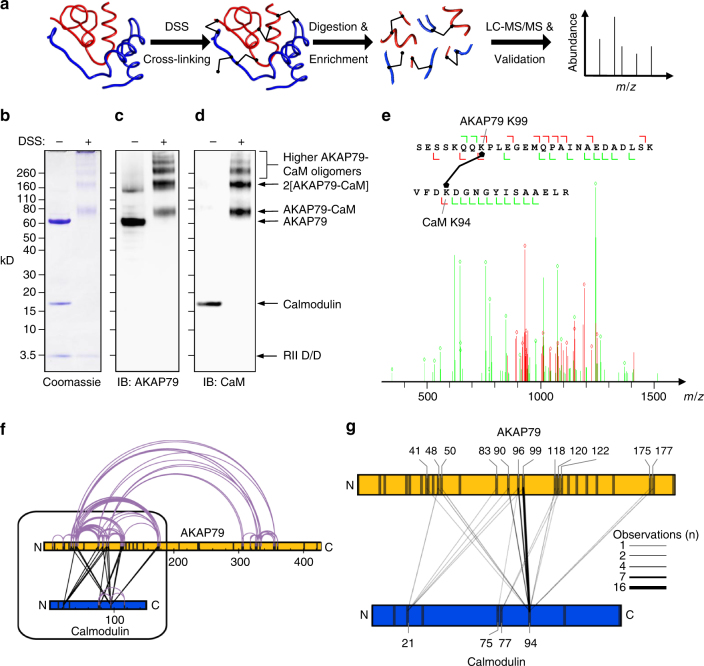
Fig. 1.
XL-MS of AKAP79 and CaM. a Schematic showing the workflow of XL-MS. Purified protein complexes are cross-linked under native conditions using an isotope-coded crosslinker. After trypsinization, potential cross-linked peptides are enriched by SEC and subsequently subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis. Cross-linked peptides are identified, sequenced and validated using the “xQuest/xProphet” pipeline. An equimolar mixture of AKAP79-D/D and CaM was separated by gel electrophoresis either before or after cross-linking and proteins were imaged by coomassie staning (b), or immunoblotting for AKAP79 (c) or CaM (d). e Exemplar MS/MS spectrum showing excellent agreement between experimental and theoretical spectra for an interlink between AKAP79K99 and CaMK94. Matches (diamonds) are indicated with a mass tolerance of 0.2 Da for common ions (green) and 0.3 Da for cross-link ions (red). f Distribution of interlinks (black) and intralinks (grey) detected in the cross-linked AKAP79-D/D-CaM sample. g Focused illustration showing distribution of interlinks between AKAP79 and CaM. Line thickness is proportional to the number of times an interlink was observed. The source data for (f) and (g) are listed in Supplementary Table 1