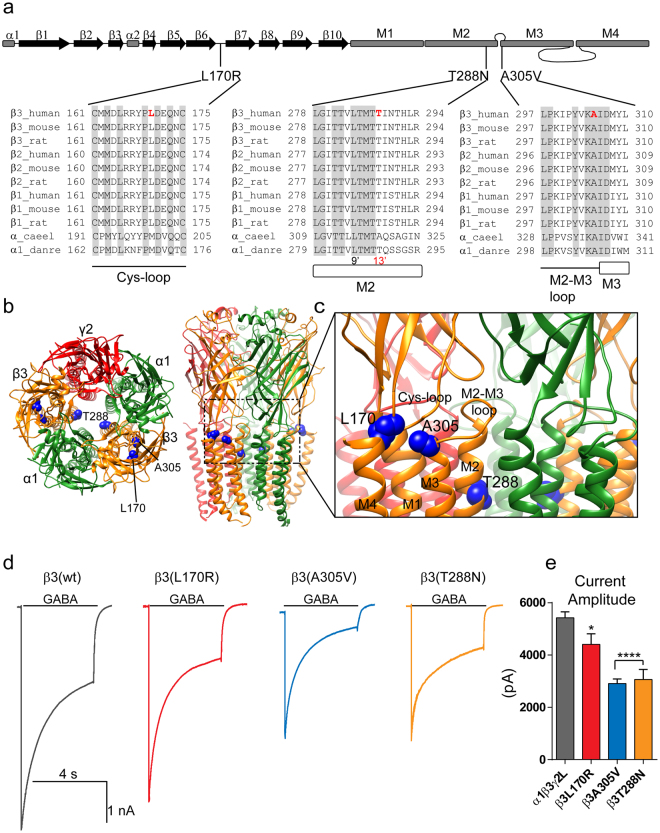
Figure 2.
β3 mutations located at the junction between the extracellular region and the transmembrane domain decreased GABAA receptor current amplitude. (a) Cartoon representation of the linearized secondary structure of the GABAA receptor β3 subunit displaying the locations of the mutations. β-strands were represented as black arrows and α-helices as gray rectangles. Human, mouse and rat β(1–3) subunits from the GABAA receptor family, and α subunits from the glutamate-gated chloride channel (α_caeel) and the glycine receptor (α1_danre) were aligned. Sites of de novo mutations in the β3 subunit were shown in red. Across all sequences, A305 is an identical residue (light gray), and L170 and T288 residues were conserved. L170 is located in the Cys-loop domain, and T288 and A305 in the transmembrane domains M2 and M3, respectively. T288 is at the 13′ position in the M2 domain (shown in red). The residues highlighted in grey were conserved across all of the subunits and pore-lining residues were numbered according to the protein sequence and position in the M2 domain. (b) 3D structural model of the α1β3γ2 GABAA receptor in the open conformational state was shown as viewed from the N-terminal extracellular (left) and transmembrane (right) sides and displaying the β subunits in orange, α subunits in green and the γ subunit in red. The β3 subunit mutations were mapped onto the structure and represented in blue. The dashed box enclosed the junction between the extracellular region and the transmembrane domain of the receptor. (c) Enlarged view of the coupling junction and the pore domain highlighting the close location of the β3 mutations with structural domains at the interface of the N-terminal (Cys-loop) and transmembrane domains (M2-M3 loop, M1, M2, M3, M4) were indicated. (d) Representative GABA-gated current traces were obtained following rapid application of 1 mM GABA for 4 s to lifted HEK293T cells voltage clamped at −20mV expressing wild-type (wt) β3 and mutant β3(L170R), β3(A305V), and β3(T288N) subunit-containing α1β3γ2L GABAA receptors. (e) Bar graphs summarized GABA-gated currents from cells expressing wild-type and mutant GABAA receptors. Values were expressed as mean ± S.E.M. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test was used to determine significance compared to the wild-type condition. ****p < 0.0001, and *p < 0.05, respectively.