Figure 4.
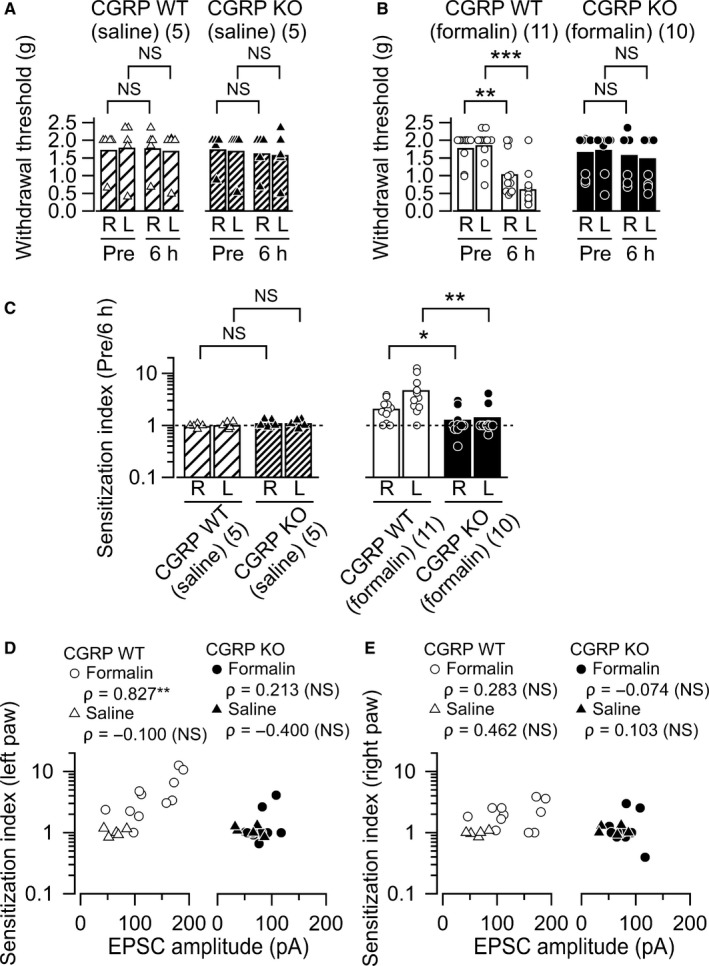
Bilateral mechanical allodynia induced by formalin. (A) and (B) Summary of the paw withdrawal threshold as measured with von Frey filaments. Left in each figure, CGRP WT mice; right in each figure, KO mice. (A) The data before (pre‐) and 6 h after saline injection; (B) the data after formalin injection. R, values from the right hind limb; L, from the left. The bars show the mean and the markers show the values from each mouse. **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; NS, not significantly different (Mann–Whitney U‐test). (C) The sensitization index (the paw withdrawal threshold at pre‐injection normalized by that at 6 h post‐injection). Left, effects of CGRP KO on the sensitization index in saline‐injected group; right, those in formalin‐injected. The sensitization index in the bilateral hind paws increased significantly following the formalin injection in the CGRP WT but not significantly in KO mice. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 (Mann–Whitney U‐test). (D) Relationship between synaptic potentiation 6 h after the injection and the sensitization index of the left paw in the CGRT WT (left) and KO (right) mice after formalin (circles) and saline (triangles) injection. Abscissa, the mean amplitude of excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) in each mouse; ordinate, the sensitization index (see Fig. 4C). There was a positive correlation between these two variables in the CGRP WT (formalin) mice (P = 0.003, n = 11). No significant correlation was found between synaptic potentiation 6 h after the injection and the sensitization index in both the CGRP WT (saline) mice and KO mice (CGRP WT [saline], P = 0.950, n = 5; CGRP KO [formalin], P = 0.554, n = 10, CGRP KO [saline], P = 0.517, n = 5). **P < 0.01 (Spearman's rank‐order correlation). NS, not significantly different. (E) Relationship between synaptic potentiation 6 h after the injection and the sensitization index of the right paw in the CGRT WT (left) and KO (right) mice after formalin (circles) and saline (triangles) injection. No significant correlation was found between synaptic potentiation 6 h after the injection and the sensitization index in both the CGRP WT and KO mice (CGRP WT [formalin], P = 0.399, n = 11; CGRP WT [saline], P = 0.434, n = 5; CGRP KO [formalin], P = 0.839, n = 10, CGRP KO [saline], P = 0.870, n = 5, Spearman's rank‐order correlation). NS, not significantly different; CGRP, calcitonin gene‐related peptide; WT, wild‐type; KO, knockout.
