Figure 2.
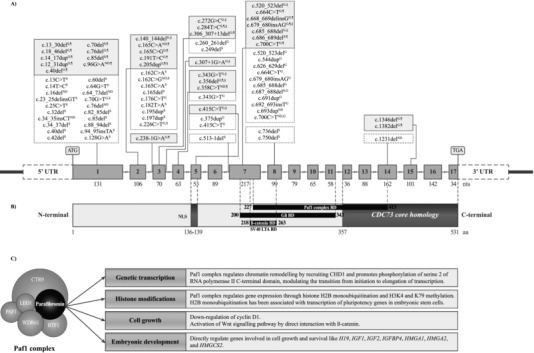
Schematic representation of the genomic organization of the human CDC73 gene, parafibromin protein, and its functions. (A) Upper panel, schematic representation of genomic structure of cell division cycle 73 (CDC73) comprising 17 exons. ATG and TGA represent the initiation and stop codons, respectively. Sites of CDC73 mutations associated with sporadic and familial parathyroid carcinoma (PC) are shown (S somatic mutation; G germline mutation; ND not defined; white, dotted line boxes, CDC73 mutations associated with sporadic PC; gray, full line boxes, CDC73 mutations associated with syndromic or hereditary forms of PC, where ¶ means hyperparathyroidism‐jaw tumor and § means familial isolated primary hyperparathyroidism). (B) Middle panel, schematic representation of parafibromin protein structure and known functional domains. CDC73 encodes a 531‐amino acid protein, whose C‐terminal domain shares 27% homology with the yeast CDC73 (CDC73 core homology domain). The nuclear localization signal (NLS) is encoded by exon 5, the evolutionary conserved polymerase‐associated factor 1 (Paf1) complex‐binding domain (Paf1 complex BD) by exons 7–14, the Gli binding domain (Gli BD) by exons 7–11, and the β‐catenin interaction binding domain (β‐catenin BD) and the SV40 large T antigen binding domain (SV40 LTA BD) by exons 7 and 8. (C) Lower panel, schematic representation of parafibromin functions. Parafibromin is a component of the Paf1 protein complex, which regulates chromatin remodeling and gene expression via histone modification. Parafibromin also regulates cell growth, via cyclin D1 and Wnt signaling, and embryonic development via genes involved in cell growth and survival. H19, H19 fetal liver mRNA; IGF1 and IGF2, insulin‐like growth factor 1 and 2; IGFBP4, insulin‐like growth factor binding protein 4; HMGA1 and HMGA2, high mobility AT‐hook 1 and 2; HMGCS2, 3‐hydroxy‐3‐methylglutaryl‐Coenzyme A synthase 2
