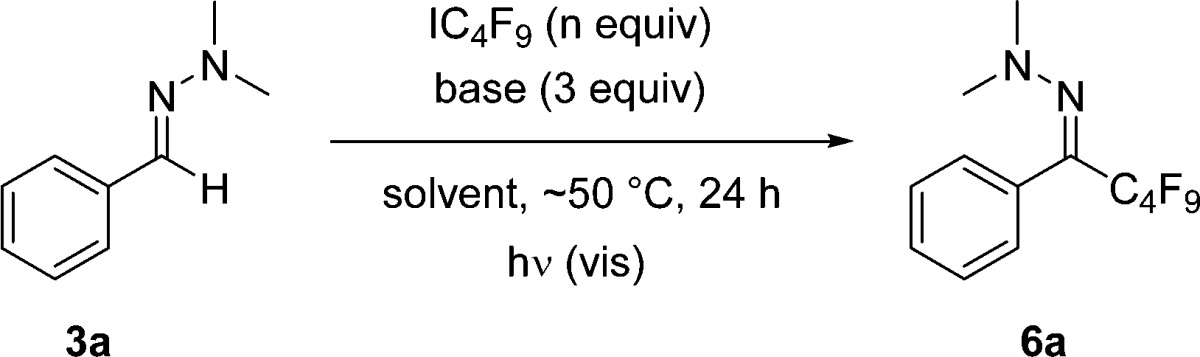Abstract
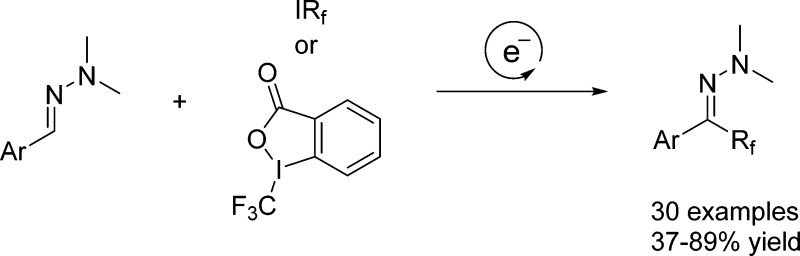
Radical trifluoromethylation of aryl N,N-dimethyl hydrazones using TBAI as an initiator and Togni’s reagent as a trifluoromethyl radical source is described. Cascades proceed via electron-catalysis; this approach is generally more applicable to hydrazone perfluoroalkylation using perfluoroalkyl iodides as the radical precursors in combination with a base under visible-light initiation.
Introduction
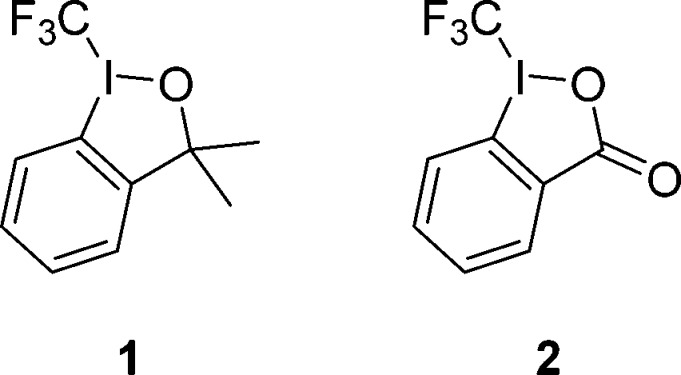
Hydrazones have been studied extensively in organic chemistry and have found wide use as pharmaceuticals,1 intermediates in the synthesis of ketones, amines, diazo compounds, hydrazines, and as chiral auxiliaries.2 The incorporation of fluorinated groups into small organic compounds has been of great interest over the past decade. The metabolic stability3 of the C–F bond, and the lipophilicity of fluorinated compounds increase the bioavailability of F-containing pharamceuticals3,4 and agrochemicals,5 thus enhancing their activity. Moreover, fluorinated building blocks have found their way into the field of modern materials science.6 Among the various F-containing substituents, the trifluoromethyl group occupies a prominent role. The introduction of the trifluoromethyl substituent can be achieved by employing ionic chemistry using nucleophilic or electrophilic trifluoromethylating reagents7 or via radical chemistry using the trifluoromethyl radical.8 Several methods have been developed over the past few years, most of which depend on the use of transition metals.9 Notably, hypervalent iodine(III) reagents such as the Togni reagents 1 and 2 have significantly contributed to the development of synthetic methodology in modern trifluoromethylation chemistry (Figure 1).10
Figure 1.
Togni’s reagents I (1) and II (2).
Recently, there have been several reports on the trifluoromethylation of hydrazones using the Togni reagent 2 in which it is mediated or catalyzed by copper-salts.11 Additionally, the perfluoroalkylation of hydrazones with perfluoroalkyl halides has been achieved by either employing photoredox catalysis using a gold complex12 or by a UV light-mediated electron-transfer process.13 We herein introduce an efficient method for transition-metal-free perfluoroalkylation of hydrazones using commercially available perfluoroalkyl iodides or the Togni reagent 2 as perfluoroalkyl radical precursors proceeding via chain processes under electron-catalysis.14
Results and Discussion
For initial studies, phenyl hydrazone 3a was chosen as a test substrate in combination with the Togni reagent 2. The results are reported in Table 1. Tetrabutylammonium iodide (TBAI) has been found to be an efficient initiator for electron-catalyzed radical-chain processes15 and was therefore also selected for the present study. The reaction of 3a with 2 (2 equiv) in 1,4-dioxane as a solvent and TBAI (0.1 equiv) at 80 °C for 2 h provided the target product 4a in a 78% yield (Table 1, entry 1).
Table 1. Optimization of the Trifluoromethylation of Hydrazones.
| entry | 2 (equiv) | TBAI (equiv) | solvent | t (h) | yielda |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.0 | 0.10 | dioxane | 2 | 78% |
| 2 | 2.0 | 0.10 | DCE | 2 | 68% |
| 3 | 2.0 | 0.10 | MeCN | 2 | 68% |
| 4 | 2.0 | 0.10 | EtOAc | 2 | 43% |
| 5 | 2.0 | 0.10 | MeCN | 7 | 66% |
| 6 | 2.0 | 0.10 | EtOAc | 7 | 82% |
| 7 | 2.0 | 0.05 | EtOAc | 7 | 33% |
| 8 | 2.0 | 0.20 | EtOAc | 7 | 55% |
| 9 | 2.0 | 0.00 | EtOAc | 7 | 5% |
| 10 | 1.0 | 0.10 | EtOAc | 16 | 63% |
| 11 | 1.2 | 0.10 | EtOAc | 16 | 88% |
| 12 | 1.5 | 0.10 | EtOAc | 16 | 71% |
| 13 | 2.0 | 0.10 | EtOAc | 24 | 11%b |
| 14 | 1.2c | 0.10 | EtOAc | 16 | 11% |
Yield determined by 19F NMR spectroscopy.
Reaction was conducted at room temperature.
Run with reagent 1 instead of 2.
As a side product, (1,4-dioxane)-2-yl ortho-iodobenzoate that was derived from Togni’s reagent and 1,4-dioxane was detected by GC–MS analysis of the reaction mixture. To suppress formation of this side product, other solvents were tested as well. Lower yields were achieved in 1,2-dichloroethane (DCE), acetronitrile, or ethyl acetate under otherwise identical conditions (Table 1, entries 2–4). In acetonitrile, increasing the reaction time from 2 to 7 h did not change the outcome, whereas in ethyl acetate the yield was significantly improved from 43 to 82% (Table 1, entries 5, 6). Increasing or decreasing the initiator loading provided a worse result and without any initiator, 3a was formed in only a 5% yield (Table 1, entries 7–9). A slight excess (1.2 equiv) of the Togni reagent 2 and a 16 h reaction time turned out to be optimal for this transformation (Table 1, entries 10–12), and we noted that trifluoromethylation does not proceed well at room temperature (Table 1, entry 13). Notably, under optimized conditions, Togni reagent 1, which is a weaker oxidant as compared to 2, delivered only 11% of the target 3a (Table 1, entry 14).
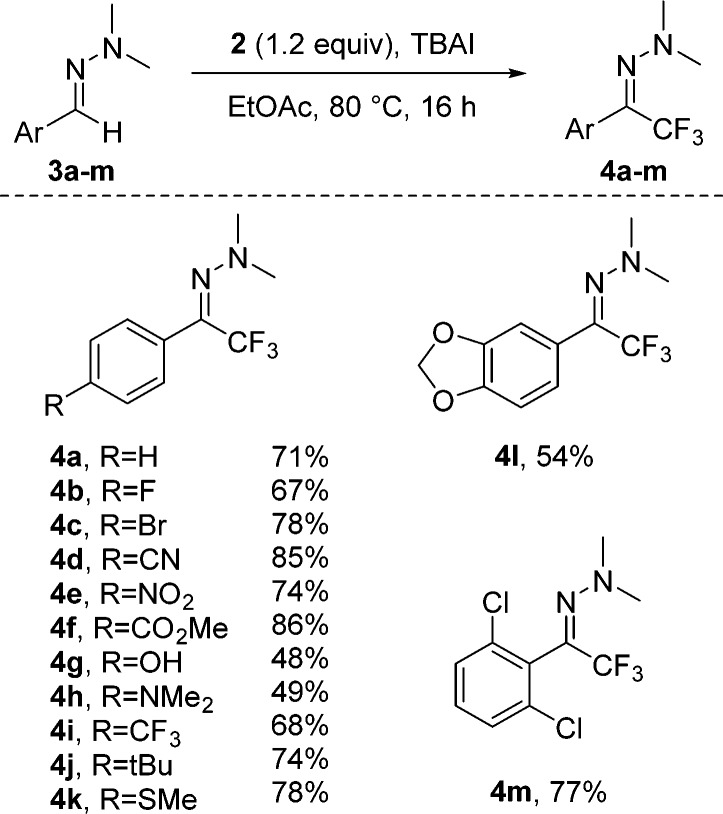
The scope of the aryl-hydrazone trifluoromethylation was found to be broad, and different substituents at the aromatic ring are tolerated. The yields given in Scheme 1 correspond to isolated yields. Because of material loss during purification resulting from the low boiling point of product 4a, the isolated yield of 4a is slightly lower than the reported NMR yield in Table 1. We also encountered similar problems for other trifluoromethylated hydrazones. Electron-withdrawing substituents such as halides (4b, 4c, 4m), the nitro (4e), and an ester group (4f), as well as the trifluoromethyl group (4i) are tolerated, and the corresponding products were obtained in good yields. The hydrazone 3g, which was bearing a phenol moiety, was successfully converted to the corresponding product 4g, albeit the yield dropped slightly (48%). For the dimethylamino-substituted hydrazone 3h, we observed competing trifluoromethylation at the aromatic ring, and the desired trifluoromethylation product 4h was isolated in a 49% yield. The disubstituted-aryl hydrazones 3l and 3m provided the target compounds 4l and 4m in moderate-to-good yields.
Scheme 1. Scope of the Trifluoromethylation.
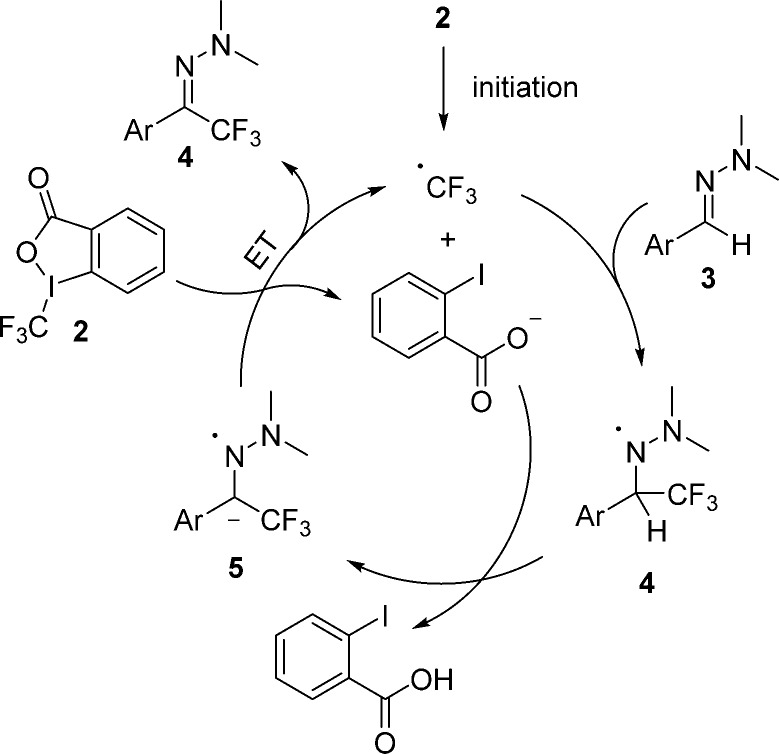
The suggested mechanism is depicted in Scheme 2. The reaction is initiated through the reduction of the Togni reagent 2 by TBAI, which acts as a formal one-electron donor15,16 to generate iodobenzoate along with the trifluoromethyl radical which will start the radical chain. The trifluoromethyl radical adds to the C=N double bond at the azomethine carbon atom of hydrazone 3 to give the hydrazinyl radical 4. The proton bound to the former azomethine carbon is strongly acidified by the neighboring radical center, and deprotonation by the iodobenzoic acid anion leads to the radical anion 5. The electron-rich radical anionic intermediate 5 then propagates the chain by single-electron transfer to the Togni reagent 2 to provide the trifluoromethyl radical and the trifluoromethylated hydrazone 4, thereby sustaining the chain.
Scheme 2. Postulated Mechanism for the Trifluoromethylation Using Togni Reagent.
Considering the strongly reducing radical anion 5 as a chain carrier in the hydrazone trifluoromethylation, we assumed that perfluoroalkyl radical generation might also be achieved with weaker-oxidizing perfluoroalkyl iodides as C-radical precursors. As compared to the I(III) reagent 2, perfluoroalkyl iodides are cheaper, and the length of the perfluoroalkyl group is readily varied by simply changing the starting iodide.
Along these lines, we continued the studies with hydrazone 3a as the test substrate in combination with commercial perfluorobutyl iodide as the Rf-radical precursor. The iodide anion generated in the SET reduction of a perfluoroalkyl iodide is a very weak base, so a stoichiometric external base has to be added to run such a cascade. For reaction optimization, the solvent and base were systematically varied (Table 2). We found that the chain can be readily initiated by simple visible-light irradiation of the reaction mixture (50 °C). In our first attempts, the cascade was performed in the presence of hexabutyl ditin as an additive to trap molecular iodine that is formed after C–I homolysis of the alkyl iodide during initiation.17 We were pleased to find that reaction of 3a with IC4F9 (2 equiv) worked well in 1,4-dioxane with 2,6-lutidine as a base (3 equiv), and the desired product 6a was formed in an 80% yield (Table 2, entry 1). A similar yield was achieved in acetonitrile, but the reaction in CHCl3 was less efficient (Table 2, entries 2, 4, and 5). In the absence of hexabutyl ditin in 1,4-dioxane, the yield dropped slightly (Table 2, entry 3). Upon switching to EtOAc as a solvent, the yield was increased to 88% (Table 2, entry 6), and increasing the excess of perfluoroalkyl iodide to 3 equiv in the absence of any ditin gave the product in a 90% yield (Table 2, entry 7). A further increase of the amount of perfluorobutyl iodide led to worse results (Table 2, entries 8 and 9). Other bases such as cesium carbonate or potassium tert-butoxide provided lower yields, likely because of solubility problems (Table 2, entries 10 and 11). However, lutidine can be replaced by imidazole without affecting the reaction outcome, but triethylamine provided a lower yield (Table 2, entries 12 and 13).
Table 2. Optimization of the Perfluoroalkylation.
| entry | solvent | base | IRF (equiv) | yielda |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | dioxane | lutidine | 2 | 80%b |
| 2 | MeCN | lutidine | 2 | 34%b |
| 3 | dioxane | lutidine | 2 | 66% |
| 4 | MeCN | lutidine | 2 | 41%b |
| 5 | CHCl3 | lutidine | 2 | 81%b |
| 6 | EtOAc | lutidine | 2 | 88%b |
| 7 | EtOAc | lutidine | 3 | 90% |
| 8 | EtOAc | lutidine | 4 | 83% |
| 9 | EtOAc | lutidine | 5 | 75% |
| 10 | EtOAc | KOtBu | 3 | 23% |
| 11 | EtOAc | Cs2CO3 | 3 | 37% |
| 12 | EtOAc | imidazole | 3 | 89% |
| 13 | EtOAc | NEt3 | 3 | 50% |
Yield determined by 19F NMR spectroscopy.
5 mol % n-Bu6Sn2 was used as additive.
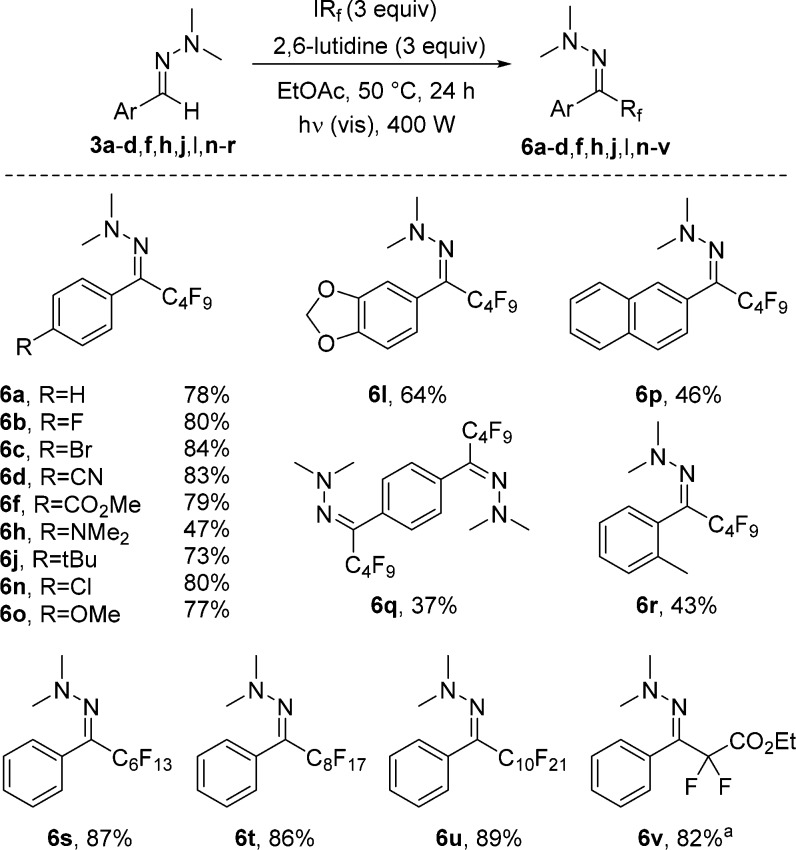
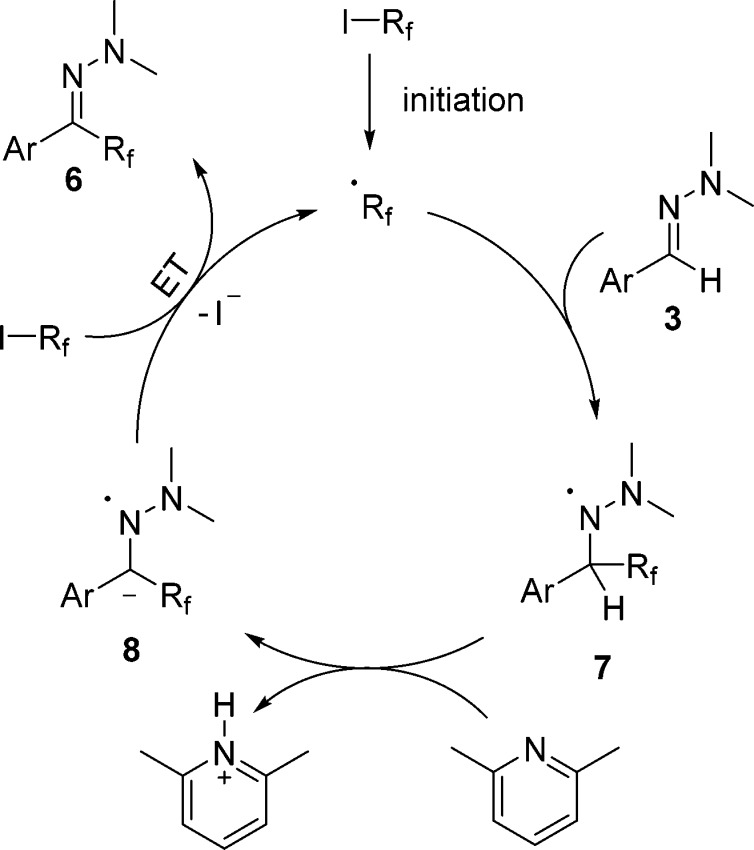
With optimized conditions established, the reaction scope was investigated. The hydrazone moiety was varied first, keeping nonafluorobutyl iodide as the C-radical precursor. The observed reactivity trends resemble those noted for the trifluoromethylation using the Togni reagent 2. This is not unexpected, as mechanistically these two processes are very similar. Hence, halogen substituents at the arene moiety in the starting aryl hydrazone are tolerated well, as documented by the successful preparation of the perfluoroalkylated hydrazones 6b, 6c, and 6n (Scheme 3). Cyano- (6d) and ester- (6f) substituted aryl hydrazones worked equally well. Also, systems bearing electron-donating substituents such as the tert-butyl (6j), the methoxy group (6o), and the acetal-conjugated congener (6l) reacted efficiently. As observed above for the other process, the amino-substituted hydrazone 3h was partially perfluoroalkylated at the arene ring, leading to a lowering of the isolated yield. Two-fold radical perfluorobutylation in a bishydrazone was possible 6q. The ortho-methylphenyl hydrazone 3r provided the target 6r in a moderate 43% yield, likely because of steric effects. For the naphthyl-substituted hydrazone 3p, the product 6p was isolated in 46% yield. The lower yield in this case is because of the limited solubility of the starting material in ethyl acetate. Employing longer-chain perfluoroalkyl iodides provides the corresponding products in good yields 6s–u. Difluoroalkylation was achieved by employing ethyl iododifluoroacetate. The corresponding difluoroalkylated product 6v was obtained in an 82% yield. The proposed mechanism (Scheme 4) for this transformation resembles the one proposed for the reaction employing the Togni reagent (compare with Scheme 2). After light-induced homolysis of the I–Rf bond (initiation), a perfluoroalkyl radical is generated, which adds to the hydrazone 3 to provide the hydrazinyl radical 7. Deprotonation of 7 by 2,6-lutidine delivers the radical anion 8, which further reacts with the perfluoroalkyl iodide by SET to product hydrazone 6, along with the perfluoroalkyl radical thereby sustaining the chain.
Scheme 3. Scope of the Perfluoroalkylation.
5 mol % of Bu6Sn2 was added.
Scheme 4. Postulated Mechanism for the Hydrazone Perfluoroalkylation Using Perfluoroalkyl Iodides.
Conclusion
In summary, two related synthetic methods for the transition-metal-free preparation of perfluoroalkylated N,N-dimethyl hydrazones were introduced by either using the Togni reagent 2 in combination with TBAI as an initiator or perfluoroalkyl iodides under visible-light initiation. The starting hydrazones are readily accessed, and perfluoroalkylated products are valuable compounds. The two methods introduced are complementary: Whereas the Togni reagent is certainly more expensive as compared to the perfluoroalkyl iodides used in the second process, the first process using the Togni reagent is recommended for trifluoromethylation because of the high volatility of the trifluoromethyl iodide, which renders experimentation difficult. However, for the higher homologues for which the corresponding Togni type reagent is either not commercially available (for example C2F5 and C3F7)18 or unknown (CnF2n+1, n > 3), the second process is clearly favored. Both cascades proceed via radical-chain reactions under electron catalysis.14a These reactions show broad substrate scope and the yields obtained are generally good.
Experimental Section
General Methods
All reactions involving air- or moisture-sensitive reagents were carried out in flame-dried glassware under an atmosphere of argon. CH2Cl2 was freshly distilled from P2O5 under argon. All other solvents and reagents were purified according to standard procedures or were used as received from Sigma-Aldrich, Acros, Alfa Aesar, or TCI Europe. 1H NMR, 19F NMR, and 13C NMR spectra were recorded on a Bruker DPX 300 at 300 K. 19F-decoupled 13C NMR spectra were recorded on an Agilent DD2 600 at 299 K. All resonances are reported relative to TMS. The spectra were calibrated relative to the solvent’s residual proton and carbon chemical shift. The coupling constants (J) are reported in Hz. Trifluorotoluene was used as the internal standard for determining the reaction yield by 19F NMR (optimization studies). Mass spectra were recorded on a Finnigan MAT 4200S, a Bruker Daltonics MicroTOF, and a Waters-Micromass Quatro LCZ (ESI); peaks are given in m/z (% of basis peak). ESI–MS (m/z) and HRMS (m/z) were performed using a Bruker MicroTOF (loop injection; resolution: 10 000), an LTQ Orbitrap XL (nanospray inlet, 1.1 kV, resolution: (30 000), and an Autoflex Speed TOF–MS (Bruker Daltonics). TLC was performed to monitor reactions using Merck silica gel 60 F-254 plates, and the detection of compounds was done using UV light. Flash column chromatography (FCC) was performed using Merck silica gel 60 (40–63 μm) to purify products, applying a pressure of about 0.2 bar. The fluorinated hydrazones were purified by MPLC using a Grace Davison Reveleris IES Flash Chromatography System with Reveleris C18-Reversed-Phase Flash Cartridges (12 g) and a flow rate of 30 mL/min with CH3CN/H2O as solvent mixture.
General Procedure 1 for the Synthesis of Hydrazones 3
Following a procedure by Ros et al.,19 the benzaldehyde derivative (1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv) was dissolved in a suspension of anhydrous MgSO4 (361 mg, 3.00 mmol, 2.00 equiv) in CH2Cl2 (10 mL). 1,1-Dimethylhydrazine (225 μL, 3.00 mmol, 2.00 equiv) was added, and the reaction was stirred for 16 h at room temperature. The MgSO4 was filtered off, and the volatiles were removed in vacuo. The pure hydrazone was obtained after flash column chromatography.
Benzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3a
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using benzaldehyde (153 μL, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (10% MTBE in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a colorless liquid (191 mg, 86%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.64–7.52 (m, 2H), 7.39–7.17 (m, 4H), 2.98 (s, 6H); 13C NMR (75 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 128.6, 127.7, 125.9, 43.1; HRMS (ESI) calcd for [C9H12N2H]+ 149.1073, found 149.1076.
4-Fluorobenzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3b
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (161 μL, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (5% EtOAc in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a brownish solid (237 mg, 95%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.64–7.41 (m, 2H), 7.21 (s, 1H), 7.07–6.88 (m, 2H), 2.95 (s, 6H); 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −114.8; HRMS (ESI) calcd for [C9H11FN2H]+ 167.0985, found 167.0955.
4-Bromobenzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3c
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 4-bromobenzaldehyde (278 mg, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (5% EtOAc in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a colorless solid (291 mg, 85%): 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.42 (s, 4H), 7.14 (s, 1H), 2.97 (s, 6H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C9H11BrN2H]+ 227.0184, found 227.0180.
4-Cyanobenzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3d
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 4-cyanobenzaldehyde (197 mg, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Crystallization from hot EtOH yielded the hydrazone as colorless crystals (207 mg, 80%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.70–7.46 (m, 4H), 7.07 (s, 1H), 3.06 (s, 6H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C10H11N3Na]+ 196.0851, found 196.0836.
4-Nitrobenzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3e
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 4-nitrobenzaldehyde (227 mg, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (30% CH2Cl2 in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as bright orange crystals (248 mg, 86%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 8.15 (d, 3J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.63 (d, 3J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.10 (s, 1H), 3.10 (s, 6H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C9H11N3O2Na]+ 216.0749, found 216.0741.
Methyl ((2,2-Dimethylhydrazono)methyl)benzoate 3f
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using Methyl 4-formylbenzoate (246 mg, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (10% EtOAc in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a colorless liquid (265 mg, 86%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.97 (d, 3J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.59 (d, 3J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.16 (s, 1H), 3.90 (s, 3H), 3.03 (s, 6H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C11H14N2O2Na]+ 229.0953, found 229.0945.
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3g
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde (183 mg, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (10% acetone in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a tan solid (217 mg, 88%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, acetone-d6, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 8.36 (s, 1H), 7.43 (d, 3J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 7.29 (s, 1H), 6.79 (d, 3J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 2.85 (s, 6H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C9H12N2OH]+ 165.1022, found 165.1035.
4-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3h
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 4-dimethylaminobenzaldehyde (224 mg, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (5% acetone in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a brown solid (177 mg, 62%): 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.47 (d, 3J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.31 (s, 1H), 6.70 (d, 3J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 2.96 (s, 6H), 2.89 (s, 6H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C11H17N3H]+ 192.1501, found 192.1484; calcd for [C11H17N3Na]+: 214.1320; found 214.1310.
4-Trifluoromethylbenzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3i
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 4-trifluoromethylbenzaldehyde (180 mg, 1.03 mmol, 1.00 equiv) with 1,1-dimethylhydrazine (150 μL, 2.07 mmol, 2.00 equiv) and MgSO4 (240 mg, 2.07 mmol, 2.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (5% MTBE in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a colorless solid (179 mg, 80%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.64 (d, 3J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.55 (d, 3J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.16 (s, 1H), 3.03 (s, 6H). 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −62.3; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C10H11F3N2H]+ 217.0953, found 217.0945.
4-tert-Butylbenzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3j
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 4-tert-butylbenzaldehyde (251 μL, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (5% EtOAc in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a colorless solid (254 mg, 83%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.51 (d, 3J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.35 (d, 3J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.27 (s, 1H), 2.94 (s, 6H), 1.32 (s, 9H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C13H20N2H]+ 205.1705, found 205.1696.
4-(Methyl)thiobenzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3k
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 4-(methyl)thiobenzaldehyde (195 μL, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (5% MTBE in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a colorless solid (257 mg, 88%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.49 (d, 3J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.26–7.15 (m, 3H), 2.96 (s, 6H), 2.48 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C10H14N2SH]+ 195.0956, found 195.0940.
Piperonal N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3l
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using piperonal (225 mg, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (5% EtOAc in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a colorless solid (243 mg, 84%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.22 (d, 4J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 7.20 (s, 1H), 6.92 (dd, 3J = 8.0, 4J = 1.6 Hz, 1H), 6.76 (d, 3J = 8.0 Hz, 1H), 5.94 (s, 2H), 2.92 (s, 6H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C10H12N2O2H]+ 193.0977, found 193.0959.
2,6-Dichlorobenzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3m
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 2,6-dichlorobenzaldehyde (263 mg, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (1% MTBE in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a colorless oil (254 mg, 78%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.30 (d, 3J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.24 (s, 1H), 7.04–7.09 (m, 1H), 3.04 (s, 6H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C9H10Cl2N2H]+ 217.0299, found 217.0305; calcd for [C9H10Cl2N2Na]+ 239.0119, found 239.0127.
4-Chlorobenzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3n
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 4-chlorobenzaldehyde (211 mg, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (5% EtOAc in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a colorless solid (216 mg, 79%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.49 (d, 3J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.28 (d, 3J = 8.5 Hz, 2H), 7.16 (s, 1H), 2.97 (s, 6H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C9H11ClN2H]+ 183.0689, found 183.0665.
4-Methoxybenzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3o
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 4-methoxybenzaldehyde (180 μL, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (5% EtOAc in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a colorless liquid (231 mg, 86%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.51 (d, 3J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.26 (s, 1H), 6.87 (d, 3J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 3.81 (s, 3H), 2.92 (s, 6H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C10H14N2OH]+ 179.1184, found 179.1163.
2-Naphthaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3p
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 2-naphthaldehyde (1.56 g, 10.0 mmol, 1.00 equiv), 1,1-dimethylhydrazine (985 μL, 13.0 mmol, 1.30 equiv), and MgSO4 (1.68 g, 20.0 mmol, 2.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (5% EtoAc in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a white solid (1.52 g, 77%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.92–7.89 (m, 1H), 7.81–7.76 (m, 4H), 7.45–7.50 (m, 3H), 3.03 (s, 6H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C13H14N2H]+ 199.1235, found 199.1226.
1,4-Phthaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3q
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 1,4-phthaldehyde (201 mg, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv), 1,1-dimethylhydrazine (450 μL, 6.00 mmol, 4.00 equiv), and MgSO4 (722 mg, 6.00 mmol, 4.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (10% MTBE in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as yellowish crystals (280 mg, 86%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.52 (s, 4H), 7.23 (s, 2H), 2.97 (s, 12H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C12H18N4H]+ 219.1610, found 219.1602.
2-Methylbenzaldehyde N,N-Dimethylhydrazone 3r
This was completed according to general procedure 1 by using 2-methylbenzaldehyde (175 μL, 1.5 mmol, 1.00 equiv). Purification by FCC (5% MTBE in pentane) yielded the hydrazone as a colorless liquid (161 mg, 66%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.83–7.71 (m, 1H), 7.43 (s, 1H), 7.24–7.08 (m, 3H), 2.99 (s, 6H), 2.42 (s, 3H); HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C10H14N2H]+ 163.1235, found 163.1205.
General Procedure 2 for the Trifluoromethylation To Give 4
The corresponding hydrazone 3 (200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) was dissolved in anhydrous EtOAc (1 mL) in a flame-dried pressure tube under argon. TBAI (7.9 mg, 20 μmol, 0.10 equiv) and 2 (76.0 mg, 240 μmol, 1.20 equiv) were added, and the reaction mixture was heated to 80 °C for 16 h. After the mixture was cooled down to room temperature, it was filtered through a short plug of silica, and the volatiles were removed in vacuo. Purification on an MPLC system using C18-reverse phase silica and CH3CN/H2O (0 min: 5% CH3CN; 40 min: 80% CH3CN; 50 min: 90% CH3CN) as the eluent afforded analytically pure trifluoromethylated hydrazones 4.
(Z)-1,1-Dimethyl-2-(2,2,2-trifluoro-1-phenylethylidene)hydrazine 4a
This was completed according to general procedure 2 by using 3a (33 μL, 0.20 mmol, 1.0 equiv). Compound 4a was obtained as a yellow oil (30.6 mg, 71%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 7.39–7.33 (m, 5H), 2.74 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 132.2, 129.7, 129.3, 129.0, 128.1, 122.0, 46.6; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = −65.7; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C10H11F3N2H]+ 217.0953, found 217.0966; calcd for [C10H11F3N2Na]+ 239.0772, found 239.0767.
(Z)-1,1-Dimethyl-2-(2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)ethylidene)hydrazine 4b
This was completed according to general procedure 2 by using 3b (33.2 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv). Compound 4b was obtained as a yellow oil (31.3 mg, 67%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 7.34 (dd, 3J = 8.6, 5.4 Hz, 2H), 7.07 (t, 3J = 8.6 Hz, 2H), 2.75 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 163.1, 131.8, 128.3, 128.2, 122.1, 115.5, 46.8; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = −65.9, −111.2; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C10H10F4N2H]+ 235.0858, found 235.0873; calcd for [(C10H10F4N2)2H]+ 469.1638, found 469.1484; calcd for [(C10H10F4N2)2Na]+ 491.1458, found 491.1547.
(Z)-1,1-Dimethyl-2-(2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(4-bromophenyl)ethylidene)hydrazine 4c
This was completed according to general procedure 2 by using 3c (45.4 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv). Compound 4c was obtained as a yellow solid (41.6 mg, 78%):1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 7.52 (d, 3J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.23 (d, 3J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 131.5, 131.5, 131.3, 127.4, 123.6, 122.0, 46.9; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = −65.6; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C10H10BrF3N2H]+ 295.0058, found 295.0067; calcd for [(C10H10BrF3N2)2H]+ 591.0017, found 590.9894; mp 51–52 °C.
(Z)-4-(1-(2,2-Dimethylhydrazono)-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)benzonitrile 4d
This was completed according to general procedure 2 by using 3d (34.6 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv). Compound 4d was obtained as a brownish solid (41.2 mg, 83%):1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.67 (d, 3J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.47 (d, 3J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 2.80 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 137.3, 131.9, 130.7, 125.3, 122.0, 118.3, 113.1, 47.2; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = −64.9; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C11H10F3N3Na]+ 264.0725, found 264.0709; calcd for [(C11H10F3N3)2Na]+ 505.1551, found 505.1496.
(Z)-1,1-Dimethyl-2-(2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(4-nitrophenyl)ethylidene)hydrazine 4e
This was completed according to general procedure 2 by using 3e (38.6 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv). Compound 4e was obtained as a yellow solid (38.6 mg, 74%):1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 8.24 (d, 3J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.54 (d, 3J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 2.82 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 148.0, 139.3, 131.0, 124.7, 123.3, 122.0, 47.3; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = −64.7; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C10H10F3N3O2H]+ 262.0803, found 262.0811; calcd for [C10H10F3N3O2Na]+ 284.0623, found 284.0636; calcd for [(C10H10F3N3O2)2Na]+ 545.1348, found 545.1401.
(Methyl (Z)-4-(1-(2,2-Dimethylhydrazono)-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)benzoate 4f
This was completed according to general procedure 2 by using 3f (41.3 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv). Compound 4f was obtained as a brownish solid (47.4 mg, 86%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 8.03 (d, 3J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.43 (d, 3J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 3.92 (s, 3H), 2.77 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 166.5, 137.1, 130.8, 130.0, 129.3, 127.1, 122.1, 52.4, 47.0; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = −65.2; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C12H13F3N2O2Na]+ 297.0827, found 297.0823; calcd for [(C12H13F3N2)2Na]+ 571.1756, found 571.1738; mp 68–69 °C.
(Z)-4-(1-(2,2-Dimethylhydrazono)-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)phenol 4g
This was completed according to general procedure 2 by using 3g (32.8 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv). Compound 4g was obtained as a brownish solid (22.1 mg, 48%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.24 (d, 3J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 6.84 (d, 3J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 5.25 (s, 1H), 2.74 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 156.4, 131.3, 130.2, 124.4, 122.1, 115.3, 46.7; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = −66.0; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C10H11F3N2OH]+ 233.0902, found 233.0917; calcd for [C10H11F3N2ONa]+ 255.0721, found 255.0749.
(Z)-4-(1-(2,2-Dimethylhydrazono)-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-N,N-dimethylaniline 4h
This was completed according to general procedure 2 by using 3h (38.3 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv). Compound 4h was obtained as a tan solid (25.3 mg, 49%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.24 (d, 3J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 6.67 (d, 3J = 8.8 Hz, 2H), 2.99 (s, 6H), 2.73 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 150.7, 132.8, 130.3, 122.2, 118.8, 111.4, 46.7, 40.3; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = −66.0; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C12H16F3N3H]+ 260.1375, found 260.1388; calcd for [C12H16F3N3Na]+ 282.1194, found 282.1189.
(Z)-1,1-Dimethyl-2-(2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)ethylidene)hydrazine 4i
This was completed according to general procedure 2 by using 3i (43.2 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv). Compound 4i was obtained as a yellow oil (38.7 mg, 68%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 7.64 (d, 3J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 7.48 (d, 3J = 8.0 Hz, 2H), 2.78 (2, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 136.3, 131.3, 130.4, 126.4, 125.2, 123.9, 122.1, 47.1; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = −63.0, −65.3; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C11H10F6N2H]+ 285.0826, found 285.0822.
(Z)-2-(1-(4-(tert-Butyl)phenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethylidene)-1,1-dimethylhydrazine 4j
This was completed according to general procedure 2 by using 3j (40.9 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv). Compound 4j was obtained as a yellow oil (40.5 mg, 74%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 7.38 (d, 3J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.27 (d, 3J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 2.73 (s, 6H), 1.33 (s, 9H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 152.4, 130.36, 129.4, 129.1, 125.2, 122.2, 46.8, 34.9, 31.4; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = −65.8; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C14H19F3N2Na]+ 295.1398, found 295.1422.
(Z)-1,1-Dimethyl-2-(2,2,2-trifluoro-1-(4-(methylthio)phenyl)ethylidene)hydrazine 4k
This was completed according to general procedure 2 by using 3k (38.9 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv). Compound 4k was obtained as a yellow oil (41.0 mg, 78%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 7.25 (d, 3J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 7.21 (d, 3J = 8.1 Hz, 2H), 2.75 (s, 6H), 2.49 (s, 3H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 140.4, 130.1, 129.2, 128.5, 125.6, 122.1, 46.8, 15.3; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = −65.7; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C11H13F3N2SH]+ 263.0830, found 263.0808; calcd for [C11H13F3N2SNa]+ 285.0649, found 285.0642.
((Z)-2-(1-(Benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethylidene)-1,1-dimethylhydrazine 4l
This was completed according to general procedure 2 by using 3l (38.4 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv). Compound 4l was obtained as a brown oil (28.0 mg, 54%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 6.86–6.73 (m, 3H), 6.00 (s, 2H), 2.77 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 148.4, 147.6, 129.2, 125.4, 123.9, 122.1, 110.0, 108.2, 101.5, 46.7; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = −65.9; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C11H11F3N2H]+ 261.0851, found 261.0854; calcd for [C11H11F3N2Na]+ 283.0670, found 283.0671.
(Z)-2-(1-(2,6-Dichlorophenyl)-2,2,2-trifluoroethylidene)-1,1-dimethylhydrazine 4m
This was completed according to general procedure 2 by using 3m (43.2 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv). Compound 4m was obtained as a dark brown solid (43.9 mg, 77%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 7.35–7.30 (m, 2H), 7.28–7.24 (m, 1H), 2.88 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = 137.2, 132.2, 131.3, 127.6, 121.9, 119.1, 45.1; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 299 K): δ (ppm) = −63.5; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C10H9Cl2F3N2Na]+ 306.9993, found 307.0002.
General Procedure 3 for the Perfluoroalkylation To Give 6
The corresponding hydrazone 3 (200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) was dissolved in anhydrous EtOAc (1 mL) in a flame-dried pressure tube under argon. 2,6-Lutidine (70 μL, 0.60 mmol, 3.0 equiv) and the corresponding perfluoroalkyl iodide (0.60 mmol, 3.0 equiv) were added. The reaction mixture was irradiated using a Philips Master HPI-T Plus 400W/645 lamp. The temperature in the photoreactor was around 50 °C (fan cooling). After 24 h of irradiation, the reaction mixture was filtered through a short plug of silica and the volatiles were removed in vacuo. Purification on an MPLC system using C18-reverse phase silica and CH3CN/H2O (0 min: 5% CH3CN; 40 min: 80% CH3CN, 50 min: 90% CH3CN) as eluent afforded analytically pure perfluoroalkylated hydrazones 6.
(E)-1,1-Dimethyl-2-(2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5-nonafluoro-1-phenylpentylidene)hydrazine 6a
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by by using 3a (33 μL, 0.20 mmol, 1.0 equiv) and nonafluorobutyl iodide (105 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6a was obtained as a yellow oil (57 mg, 78%). Spectral data are in accordance with literature reports:131H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.37–7.21 (m, 5H), 2.70 (s, 6H); 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −81.2, −105.3, −120.0, −124.4.
(E)-1,1-Dimethyl-2-(2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5-nonafluoro-1-(4-fluorophenyl)pentylidene)hydrazine 6b
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3b (33.2 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) and nonafluorobutyl iodide (105 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6b was obtained as a yellow oil (61.1 mg, 80%). Spectral data are in accordance with literature reports:131H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.24–7.18 (m, 2H), 7.06–6.90 (m, 2H), 2.68 (s, 6H); 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −81.2, −105.4, −111.3, −120.1, −124.5.
(E)-2-(1-(4-Bromophenyl)-2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5-nonafluoropentylidene)-1,1-dimethylhydrazine 6c
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3c (45.4 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) and nonafluorobutyl iodide (105 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6c was obtained as a yellow oil (74.5 mg, 84%). Spectral data are in accordance with literature reports:131H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.50 (d, 3J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.19 (d, 3J = 8.4 Hz, 2H), 2.77 (s, 6H); 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −81.1, −105.3, −120.1, −124.5.
(E)-4-(1-(2,2-Dimethylhydrazono)-2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5-nonafluoropentyl)benzonitrile 6d
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 4-cyanobenzaldehyde hydrazone 3d (34.6 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) and nonafluorobutyl iodide (105 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6d was obtained as a yellow solid (65.1 mg, 83%). Spectral data are in accordance with literature reports:131H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.66 (d, 3J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 7.44 (d, 3J = 8.3 Hz, 2H), 2.80 (s, 6H); 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −81.2, −104.8, −120.2, −124.6.
Methyl (E)-4-(1-(2,2-Dimethylhydrazono)-2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5-nonafluoropentyl)benzoate 6f
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3f (41.3 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) and nonafluorobutyl iodide (105 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6f was obtained as a yellow solid (67.6 mg, 79%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 8.07–7.97 (m, 2H), 7.42–7.37 (m, 2H), 3.93 (s, 3H), 2.77 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm) = 166.6, 130.6, 129.2, 126.1, 117.8, 114.0, 111.5, 109.2, 52.4, 46.8; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −81.2, −105.0, −120.1, −124.5; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C15H13F9N2Na]+: 447.0731, found 447.0742; calcd for [(C15H13F9N2)Na]+ 871.1564, found 871.1562; mp 26–27 °C.
(E)-4-(1-(2,2-Dimethylhydrazono)-2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5-nonafluoropentyl)-N,N-dimethylaniline 6h
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3h (38.3 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) and nonafluorobutyl iodide (105 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6h was obtained as a yellow solid (38.2 mg, 47%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.16 (d, 3J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 6.66 (d, 3J = 8.9 Hz, 2H), 2.99 (s, 6H), 2.73 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm) = 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −81.2, −105.8, −120.0, −124.4; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C15H16F9N3H]+ 410.1279, found 410.1276; calcd for [C15H16F9N3Na]+ 432.1098, found 432.1095.
(E)-2-(1-(4-(tert-Butyl)phenyl)-2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5-nonafluoropentylidene)-1,1-dimethylhydrazine 6j
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3j (40.9 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) and nonafluorobutyl iodide (105 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6j was obtained as a yellow solid (61.6 mg, 73%): 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.41–7.31 (m, 2H), 7.28–7.19 (m, 2H), 2.73 (s, 6H), 1.33 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm) = 152.2, 129.8, 129.1, 129.0, 124.8, 117.7, 113.9, 111.4, 109.1, 46.4, 42.7, 34.7, 31.2; 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −81.2, −105.3, −120.0, −124.4; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C17H19F9N2Na]+ 445.1302, found 445.1307; mp 25–27 °C.
(E)-2-(1-(Benzo[d][1,3]dioxol-5-yl)-2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5-nonafluoropentylidene)-1,1-dimethylhydrazine 6l
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3l (38.4 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) and nonafluorobutyl iodide (105 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6l was obtained as a yellow oil (52.6 mg, 73%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 6.85–6.71 (m, 3H), 6.00 (s, 2H), 2.78 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm) = 148.3, 147.4, 128.0, 125.5, 124.55, 117.8, 114.0, 111.6, 110.6, 109.2, 108.0, 101.5, 46.5; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −81.2, −105.4, −120.0, −124.4; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C14H11F9N2H]+ 411.0755, found 411.0627; calcd for [C14H11F9N2Na]+ 433.0575, found 433.0566.
(E)-2-(1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5-nonafluoropentylidene)-1,1-dimethylhydrazine 6n
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3n (36.5 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) and nonafluorobutyl iodide (105 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6n was obtained as a yellow oil (63.9 mg, 80%). Spectral data are in accordance with literature reports:131H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.40–7.29 (m, 2H), 7.28–7.28 (m, 2H), 2.77 (t, 6H); 19F NMR (282 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −81.2, −105.3, −120.1, −124.5.
(E)-1,1-Dimethyl-2-(2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5-nonafluoro-1-(4-methoxyphenyl)pentylidene)hydrazine 6o
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3o (35.7 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) and nonafluorobutyl iodide (105 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6o was obtained as a yellow oil (56.0 mg, 77%). Spectral data are in accordance with literature reports:131H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.23 (d, 3J = 8.7 Hz, 2H), 6.93–6.82 (m, 2H), 3.83 (s, 3H), 2.74 (s, 6H); 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −81.19, −105.63, −120.07, −124.44.
(E)-1,1-Dimethyl-2-(2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5-nonafluoro-1-(naphthalen-2-yl)pentylidene)hydrazine 6p
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3p (39.7 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) and nonafluorobutyl iodide (105 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6p was obtained as a yellow oil (38.4 mg, 46%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.88–7.84 (m, 2H), 7.84–7.82 (m, 1H), 7.81–7.80 (m, 1H), 7.57–7.49 (m, 2H), 7.43 (m, 1H), 2.77 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm) = 133.1, 132.4, 129.8, 129.7, 128.3, 128.1, 127.7, 127.5, 127.3, 127.0, 126.6, 117.7, 114.0, 111.4, 109.1, 46.6; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −81.1, −105.0, −119.9, −124.4; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C17H13F9N2H]+ 417.1013, found 417.0999; calcd for [C17H13F9N2Na]+ 439.0833, found 439.0822.
1,4-Bis((E)-1-(2,2-dimethylhydrazono)-2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5-nonafluoropentyl)benzene 6q
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3q (43.7 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) and nonafluorobutyl iodide (105 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6q was obtained as a yellow solid (48.0 mg, 37%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.31 (s, 4H), 2.76 (s, 12H).13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm) = 133.2, 129.8, 126.7, 117.6, 113.8, 111.3, 109.0, 46.5.19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −81.2, −105.3, −120.1, −124.5; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C20H16F18N4Na]+ 677.0985, found 677.0989; mp 63–64 °C.
(E)-1,1-Dimethyl-2-(2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,5-nonafluoro-1-(o-tolyl)pentylidene)hydrazine 6r
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3r (32.5 mg, 200 μmol, 1.00 equiv) and nonafluorobutyl iodide (105 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6r was obtained as a yellow oil (32.8 mg, 37%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.28 (td, 3J = 7.5 Hz, 4J = 1.5 Hz, 1H), 7.25 (d, 3J = 7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.22–7.17 (m, 1H), 7.19–7.13 (m, 1H), 2.72 (s, 6H), 2.24 (s, 3H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm) = 138.9, 131.9, 130.5, 129.5, 129.3, 127.8, 125.0, 117.7, 114.3, 111.5, 109.1, 45.7, 19.8; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −81.2, −104.8, −119.7, −123.9; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C14H13F9N2H]+ 381.1013, found 381.1009; calcd for [C14H13F9N2Na]+:403.0833, found 403.0824.
(E)-1,1-Dimethyl-2-(2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,7-tridecafluoro-1-phenylheptylidene)hydrazine 6s
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3a (33 μL, 0.20 mmol, 1.0 equiv) and perfluorohexyl iodide (130 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6s was obtained as a orange oil (81.4 mg, 87%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.39–7.32 (m, 3H), 7.34–7.29 (m, 2H), 2.74 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm) = 132.5, 130.5, 129.2, 128.5, 128.1, 118.4, 116.5, 114.1, 111.5, 110.6, 108.9, 108.6, 46.6; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −80.9, −105.2, −119.3, −120.5, −122.8, −126.1; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C15H11F13N2Na]+ 489.0612, found 489.0619.
(E)-2-(2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,9,9,9-Heptadecafluoro-1-phenylnonylidene)-1,1-dimethylhydrazine 6t
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3a (33 μL, 0.20 mmol, 1.0 equiv) and perfluorooctyl iodide (160 μL, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6t was obtained as a orange oil (97.1 mg, 86%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.39–7.33 (m, 3H), 7.33–7.28 (m, 2H), 2.74 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm) = 132.3, 130.3, 129.0, 128.3, 127.9, 117.1, 113.9, 111.9, 111.3, 111.0, 110.8, 110.2, 108.4, 46.4; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −80.9, −105.2, −119.3, −120.4, −121.9, −122.8, −126.2; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C17H11F17N2H]+ 567.0729, found 567.0739; calcd for [C17H11F17N2Na]+ 589.0548, found 589.0567.
(E)-2-(2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5,6,6,7,7,8,8,9,9,10,10,11,11,11-Henicosafluoro-1-phenylundecylidene)-1,1-dimethylhydrazine 6u
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3a (33 μL, 0.20 mmol, 1.0 equiv) and perfluorodecyl iodide (366 mg, 600 μmol, 3.00 equiv). Compound 6u was obtained as a purple solid (119 mg, 89%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.39–7.32 (m, 3H), 7.33–7.28 (m, 2H), 2.74 (s, 6H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm) = 132.3, 130.3, 128.9, 128.4, 127.9, 117.1, 113.9, 111.9, 111.3, 111.0, 110.9, 110.8, 110.7, 110.2, 108.3, 46.4; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −80.9, −105.3, −119.3, −120.3, −121.8, −122.8, −126.2; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C19H11F21N2H]+ 667.0665, found 667.0679; calcd for [C19H11F21N2Na]+ 689.0485, found 689.0501; mp 37–39 °C.
Ethyl (E)-3-(2,2-Dimethylhydrazono)-2,2-difluoro-3-phenylpropanoate 6v
This was completed according to general procedure 3 by using 3a (3 μL, 0.20 mmol, 1.0 equiv), ethyl iododifluoroacetate (88 μL, 0.60 mmol, 3.0 equiv), and hexabutylditin (5 μL, 0.02 mmol, 0.1 equiv). The compound was purified using a Reveleris Amino 4 g column. Compound 6v was obtained as a yellow oil (44.3 mg, 82%): 1H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K): δ (ppm) = 7.43–7.33 (m, 5H), 4.38 (q, 3J = 7.1 Hz, 2H), 2.68 (s, 6H), 1.39 (t, 3J = 7.1 Hz, 3H); 13C{1H, 19F} NMR (151 MHz, CDCl3) δ (ppm) = 164.4, 134.0, 131.9, 129.9, 129.1, 128.1, 115.3, 62.5, 46.6, 14.2; 19F NMR (564 MHz, CDCl3, 300 K) δ (ppm) = −100.1; HRMS (ESI): calcd for [C13H16F2N2H]+ 271.1253, found 271.1264.
Acknowledgments
We thank the European Research Council (ERC Advanced Grant agreement No. 692640) for financial support.
Supporting Information Available
The Supporting Information is available free of charge on the ACS Publications website at DOI: 10.1021/acs.joc.7b00934.
NMR spectra (PDF)
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Supplementary Material
References
- Verma G.; Marella A.; Shaquiquzzaman M.; Akhtar M.; Ali M. R.; Alam M. M. J. Pharm. BioAllied Sci. 2014, 6, 69–80. 10.4103/0975-7406.129170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazny R.; Nodzewska A. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 1386–1434. 10.1021/cr900067y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki T.; Taguchi T.; Ojima I. In Fluorine in Medicinal Chemistry and Chemical Biology; Ojima I., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- a Purser S.; Moore P. R.; Swallow S.; Gouverneur V. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 320–330. 10.1039/B610213C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Müller K.; Faeh C.; Diederich F. Science 2007, 317, 1881–1886. 10.1126/science.1131943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Shimizu M.; Hiyama T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 214–231. 10.1002/anie.200460441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeschke P. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 570–589. 10.1002/cbic.200300833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Hiyama T. In Organofluorine Compounds: Chemistry and Application; Yamamoto H., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, 2000. [Google Scholar]; b Hird M. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 2070–2095. 10.1039/b610738a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X.; Xu C.; Wang M.; Liu Q. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 683–730. 10.1021/cr400473a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Studer A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8950–8958. 10.1002/anie.201202624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Zhang C. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 2895–2906. 10.1002/adsc.201400370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Barata-Vallejo S.; Lantaño B.; Postigo A. Chem. - Eur. J. 2014, 20, 16806–16829. 10.1002/chem.201404005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Liang T.; Neumann C. N.; Ritter T. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8214–8264. 10.1002/anie.201206566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Merino E.; Nevado C. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6598–6608. 10.1039/C4CS00025K. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Egami H.; Sodeoka M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 8294–8308. 10.1002/anie.201309260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpentier J.; Früh N.; Togni A. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 650–682. 10.1021/cr500223h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Pair E.; Monteiro N.; Bouyssi D.; Baudoin O. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 5346–5349. 10.1002/anie.201300782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Prieto A.; Jeamet E.; Monteiro N.; Bouyssi D.; Baudoin O. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 4770–4773. 10.1021/ol5022228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Prieto A.; Landart M.; Baudoin O.; Monteiro N.; Bouyssi D. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2015, 357, 2939–2943. 10.1002/adsc.201500237. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Xie J.; Zhang T.; Chen F.; Mehrkens N.; Rominger F.; Rudolph M.; Hashmi A. S. K. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2934–2938. 10.1002/anie.201508622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie J.; Li J.; Wurm T.; Weingand V.; Sung H.-L.; Rominger F.; Rudolph M.; Hashmi A. S. K. Org. Chem. Front. 2016, 3, 841–845. 10.1039/C6QO00158K. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- a Studer A.; Curran D. P. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 765–773. 10.1038/nchem.2031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Studer A.; Curran D. P. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 58–102. 10.1002/anie.201505090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B.; Mück-Lichtenfeld C.; Daniliuc C. G.; Studer A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10792–10795. 10.1002/anie.201306082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leifert D.; Artiukhin D. G.; Neugebauer J.; Galstyan A.; Strassert C. A.; Studer A. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 5997–6000. 10.1039/C6CC02284G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Curran D. P.; Chen M.-H.; Kim D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1989, 111, 6265–6276. 10.1021/ja00198a043. [DOI] [Google Scholar]; b Curran D. P.; Chang C.-T. Tetrahedron Lett. 1990, 31, 933–936. 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)94396-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y.; Studer A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8221–8224. 10.1002/anie.201202623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ros A.; Estepa B.; López-Rodríguez R.; Álvarez E.; Fernández R.; Lassaletta J. M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2011, 49, 11724–11728. 10.1002/anie.201104544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.