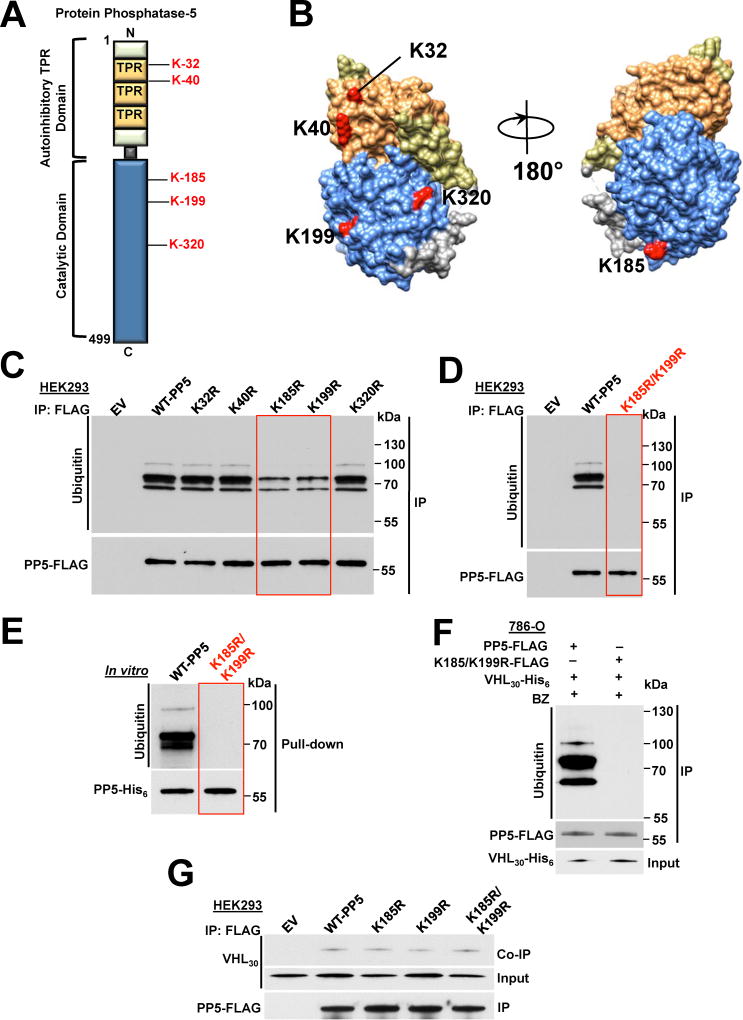
Figure 4. VHL-mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of K185/K199-PP5. See also Figure S4.
A) Schematic representation of PP5 with highlighted lysine residues possibly subject to VHL mediated ubiquitination.
B) Potential ubiquitinating lysine residues are highlighted on the cartoon representation of the PP5 protein modeled with UCSF Chimera software (PDB:1WAO). Color-coded as in Figure 1D.
C) Wild-type PP5-FLAG and its potentially non-ubiquitinating lysine mutants were transiently expressed and immunoprecipitated (IP) from HEK293 cells. Ubiquitination of PP5 was examined by immunoblotting. Empty vector (EV) was used as a control.
D) Wild-type PP5-FLAG and its non-ubiquitinating K185/K199R mutant were transiently expressed and IP from HEK293 cells. Ubiquitination of PP5 was examined by immunoblotting anti-ubiquitin antibody. Empty vector (EV) was used as a control.
E) Recombinant PP5-His6 and K185/K199R double mutant were used in an in vitro ubiquitination assay with VCB-Cul2 (VHL30-Elongin C-Elongin B-Cullin-2) and Rbx1, which acts as an ubiquitin-ligase (E3). Ubiquitination of PP5 was assessed with immunoblotting.
F) PP5-FLAG or K185/K199R-PP5-FLAG double mutant were co-transfected with VHL30-His6 in 786-O cells and then after 24 hr treated with 50 nM BZ for 2 hr. PP5-FLAG or K185/K199R-PP5-FLAG was IP and ubiquitination was assessed by immunoblotting.
G) PP5-FLAG, K185-PP5-FLAG, K199R-PP5-FLAG, K185/K199R-PP5-FLAG and empty vector (EV) were individually and transiently expressed in HEK293 cells. They were IP and their interactions with VHL30 were assessed in the Co-IP by immunoblotting.