Figure 7. SMURF1 Controls Mycobacterial Growth in Human Macrophages, is Expressed in Granulomas, and Colocalizes with M. tuberculosis in Lungs of Patients with Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis.
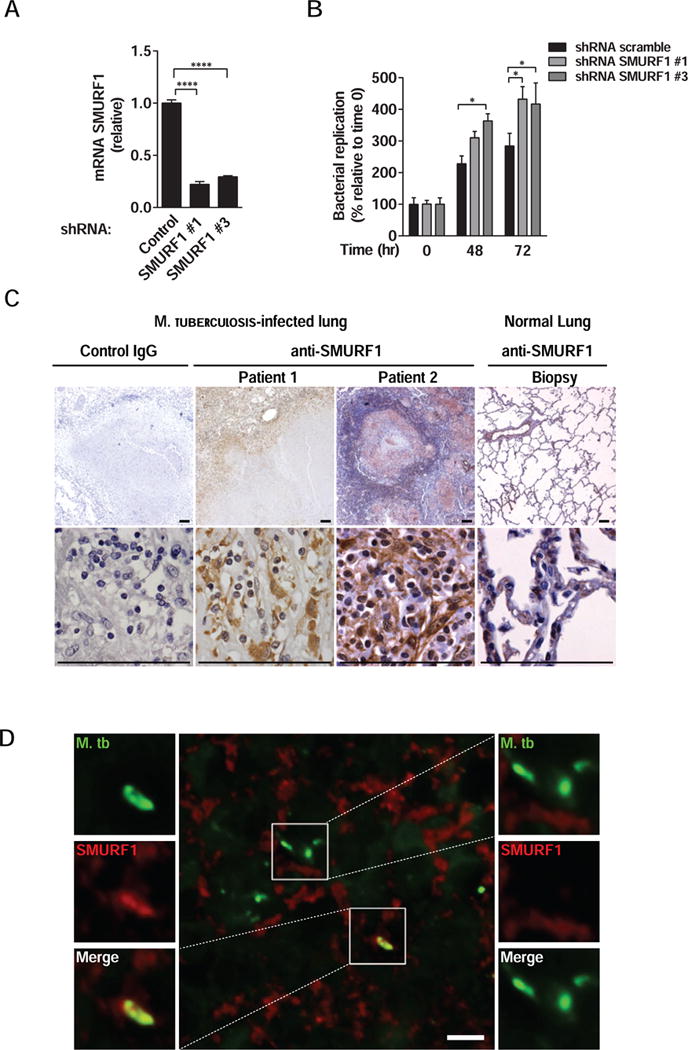
(A) Smurf1 knockdown in primary human monocyte-derived macrophages transduced with controls or two different SMURF1 shRNA constructs. mRNA levels of SMURF1 were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR. Bars represent mean ± SEM (normalized to control scrambled shRNA). Similar results were observed in three independent experiments. ****P<0.0001; t-test.
(B) Mtb growth in primary human monocyte-derived macrophages transduced with control scrambled or SMURF1shRNA. Infected cells were lysed at the indicated time-points and Mtb growth was determined by counting CFUs. Bars are mean ± SEM of quadruplicate samples; each sample was normalized to day 0. Similar results were observed in two independent experiments. See Figure S5A for results from one additional donor. *P<0.05; **P<0.01 for indicated comparison; two-way ANOVA.
(C) Immunohistochemical staining for SMURF1 in lung biopsies of two human patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis or from a normal lung. Scale bars, 100 μm.
(D) Immunofluorescence staining of a lung biopsy of a human patient with active pulmonary tuberculosis using anti-Mtb and anti-SMURF1 antibodies. Left panel, image of Mtb that colocalizes with SMURF1. See Figure S5 for additional examples. Right panel, image of Mtb that do not colocalize with SMURF1. Scale bar, 5 μm. See also Figure S5.
