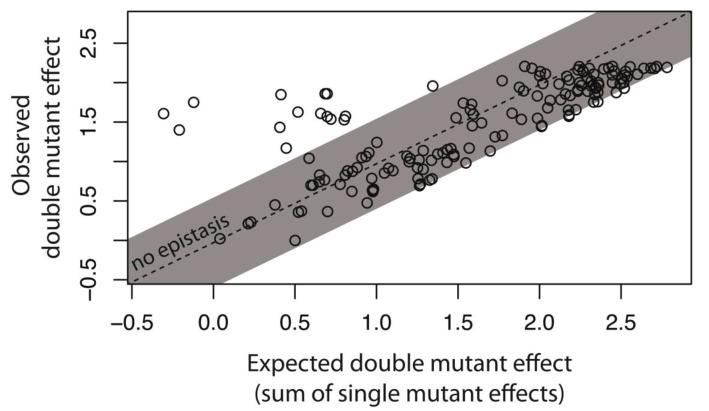
Figure 6. Not all intermolecular epistasis can be explained by accounting for the underlying genetic regulatory structure of the system.
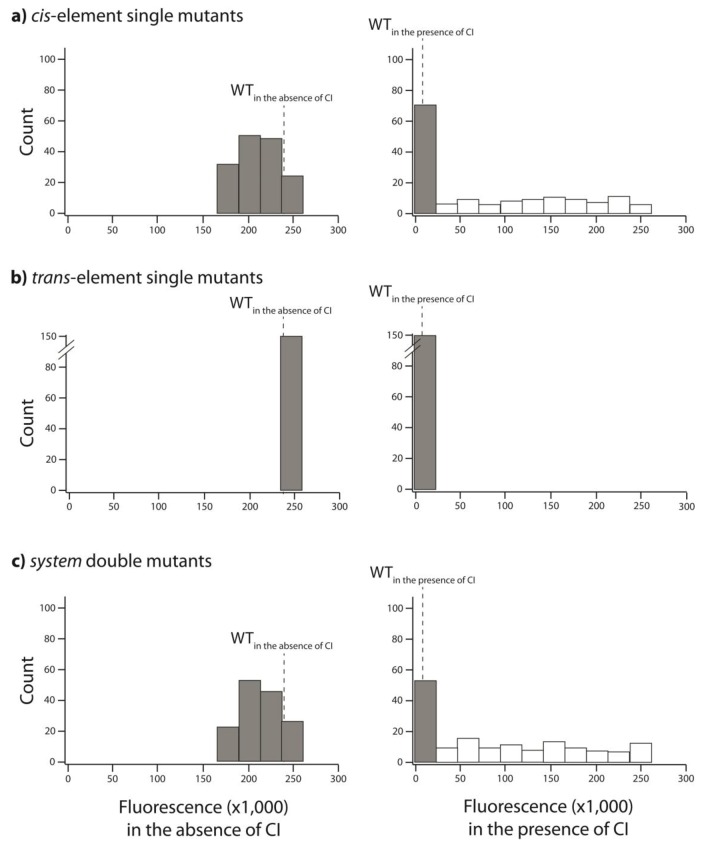
We created 150 double mutants with single mutation combinations corresponding to Figure 5G. A double mutant in this library would not be in epistasis unless a mutation in trans binds the cis mutant differently than the wildtype trans does. In a plate reader, we measured expression levels of monoclonal populations of each double mutant and its constitutive single mutants in the presence of CI. Epistasis was estimated as the deviation of the observed double mutant effect from the additive expectation based on single mutant effects. The grey bar indicates measurements that are not in significant epistasis. The effects of single mutations in cis and in trans, as well as the double mutant effects, are shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 1, while the underlying data are shown in Figure 6—source data 1. The location of point mutations is shown in Figure 6—figure supplement 2 and Figure 6—source data 2.