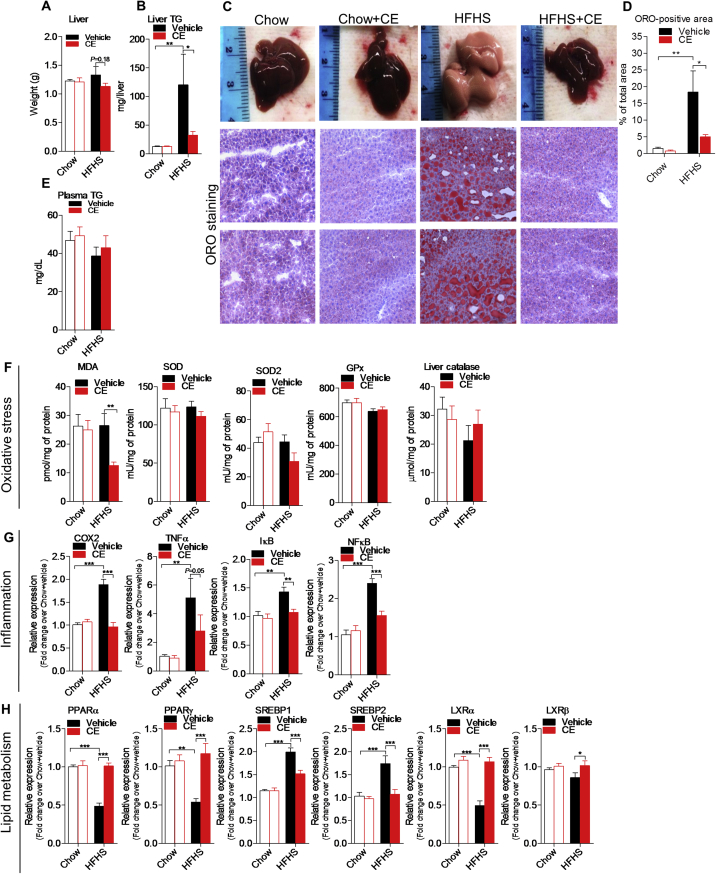
Figure 2.
CE reverses hepatic steatosis and alleviates liver inflammation. (A) Liver weight, (B) hepatic triglyceride accumulation, (C) representative images of hepatic lipid accumulation by oil red O (ORO) staining, (D) quantification of ORO-positive area, and (E) plasma triglycerides. (F) Hepatic quantification of [MDA] malondialdehyde, [SOD] superoxide dismutase, [GPx] glutathione peroxidase, and catalase. (G) Liver mRNA expression of [COX2] cyclooxygenase 2, [TNFα] tumor necrosis factor α, [NFκB], nuclear factor κ-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, [IκB] NFκB inhibitor. (H) Liver mRNA expression of [PPARα/γ] peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α and γ, [SREBP1c/2] sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c and 2 and [LXRα/β] liver X receptor α and β. Two-way ANOVA with a Student-Newman-Keuls post hoc test was applied to calculate the significance of the differences between groups. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM; n = 8–11; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.