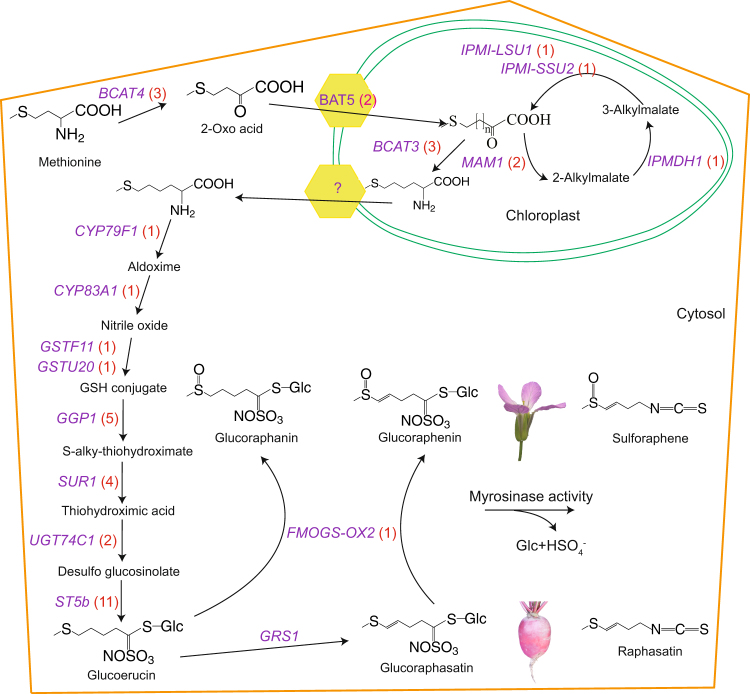
Figure 2.
Putative aliphatic GSL biosynthetic and degradation pathways in R. sativus. Glucoraphasatin is principally found in the root of R. sativus, whereas glucoraphenin is detected mainly in the flowers. The genes shown in purple represent the genes involved in aliphatic GSL biosynthesis in R. sativus, and the numbers in the red brackets are the numbers of corresponding genes in R. sativus. The yellow polygon stands for the translocator on the chloroplast membrane. The symbol ‘?’ represents unknown genes.