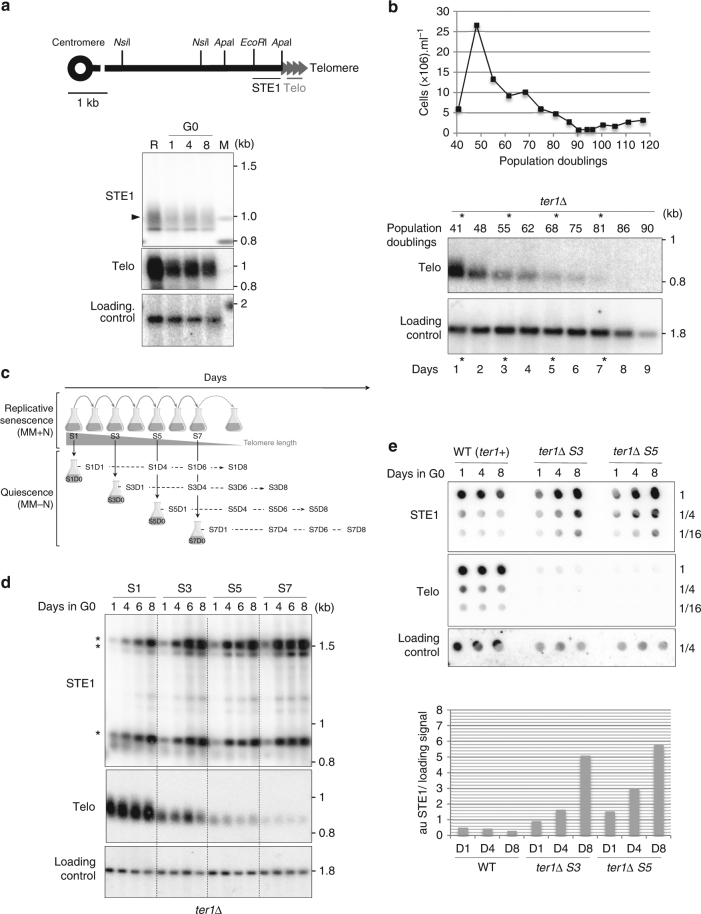
Fig. 1.
Eroded telomeres are rearranged in quiescence. a Top, relative position of the restriction sites in the telomeric and subtelomeric regions of S. pombe chromosomes based on pNSU70. Telomeric (Telo) and subtelomeric (STE1) probes used for southern blot are represented. Bottom, genomic DNA from WT cells was digested with EcoRI and southern blotted. The membrane was hybridized with Telo, STE1, and chromosomic probes. R, replicative sample; M, molecular weight marker; 1, 4, 8 correspond to the number of days in quiescence. A chromosomal probe was used as a loading control. b Top, freshly deleted ter1 colony was maintained in exponential phase in liquid EMM medium for about 120 generations by serial dilutions. Population doublings were monitored by cell counting. Bottom, genomic DNA was digested with EcoRI and southern blotted. The membrane was hybridized with Telo and chromosomal probes. Asterisks indicate the time points of the replicative senescence kinetics that have been shifted to nitrogen-deprived medium. c Schematic representation of a typical senescence-quiescence coupled experiment. Cells collected at different type points of the senescence were shifted in deprived-nitrogen medium and maintained in senescence as indicated. d Genomic DNA from quiescent ter1Δ cells was digested by EcoRI and southern blotted. Membrane was hybridized with Telo, STE1, and chromosomal probes. 1, 4, 6, 8 correspond to number of days for which cells were in G0 before collecting. S1, S3, S5, and S7 indicate the days during the senescence kinetics at which cells were starved from nitrogen. Subtelomeric rearrangements are shown by asterisks. e Genomic DNA from quiescent WT and ter1Δ cells at S3 and S5 was spotted onto Hybond-XL membrane and hybridized with the indicated probes. Signal quantification has been performed with “Quantity one” software and STE1/Control ratio was determined