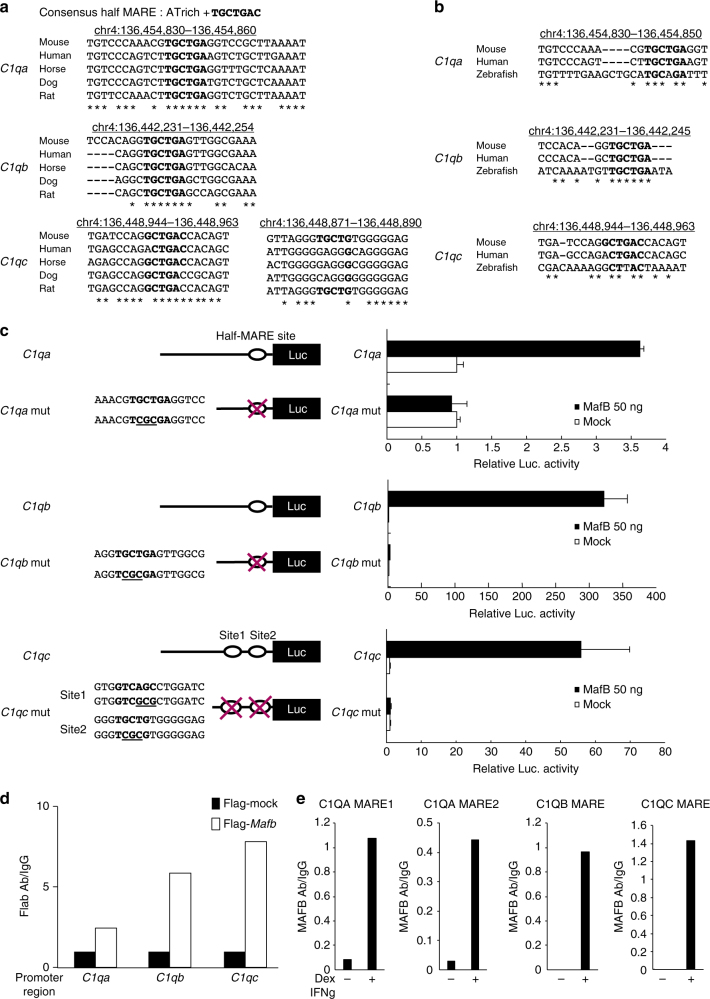
Fig. 3.
MafB directly regulates C1qa, C1qb, C1qc genes. a Half of the Maf recognition elements (half-MARE) were identified in C1q gene promoters using the UCSC Genome Browser. The half-MARE site in the C1q gene promoters (bold) was highly conserved among mammalian species. b Half-MARE was also conserved in zebrafish. c A MafB-expressing vector was co-transfected with luciferase reporter constructs of C1qa, C1qb, or C1qc promoter containing a MARE site or a mutant MARE site into RAW264.7 cells. The luciferase activity was analyzed after a 24 h transfection. The term “mut” indicates mutation in the MARE sites. Data are presented as the means ± s.e.m. of duplicates. The data are from one experiment that is representative of at least two independent experiments. d A ChIP assay was conducted using RAW264.7 cells. Flag-mock and Flag-MafB-expressing vectors were transfected into the cells. After 24 h, chromatin from the transfected cells was precipitated with anti-Flag and anti-IgG. The half-MARE sequences in the C1q gene promoters were amplified and analyzed by qPCR. The data are from one experiment that was representative of at two independent experiments. e A ChIP assay was conducted using THP-1 cells. The cells were collected after they were treated with or without dexamethasone (Dex) and IFNγ, and then chromatin was precipitated with anti-MAFB and anti-IgG. The half-MARE sequences in the C1q gene promoters were amplified and analyzed by qPCR. The data are from one experiment that was representative of two independent experiments