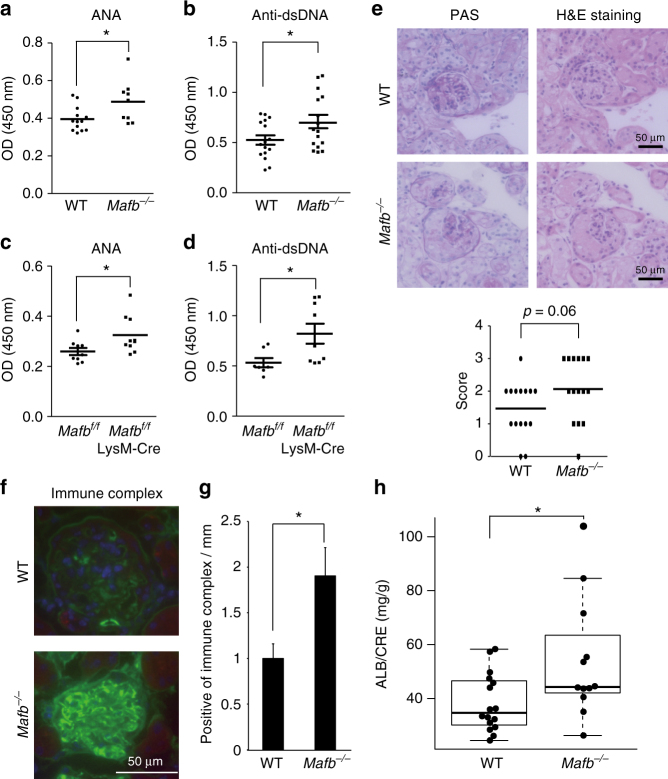
Fig. 6.
Mafb −/− mice develop autoimmune disease. a ELISA analysis showed the ANA levels in serum from 6 to 12-month-old transplanted mice (WT, n = 13; Mafb −/−, n = 9). b The production of anti-ds-DNA was observed in serum (n = 16 for each genotype). c The ANA level of Mafb f/f::LysM-Cre and Mafb f/f were analyzed by ELISA (Mafb f/f, n = 9; Mafb f/f::LysM-Cre, n = 10). d Serum anti-ds-DNA was analyzed by ELISA (Mafb f/f, n = 7; Mafb f/f::LysM-Cre, n = 9). a–d The results of duplicate independent experiments were pooled. e Kidneys were stained with PAS and HE staining. Glomerulonephritis was scored from 0 to 3 in a blinded test (WT, n = 16; Mafb −/−, n = 15). The data were analyzed with the Brunner–Munzel test. f The deposition of immune complexes in glomeruli was assayed for the immune complex (IgG + IgM + IgA). g Immune complex-positive glomeruli were quantified (WT, n = 5; Mafb −/−, n = 5). h Urinary protein was measured in WT and Mafb −/− 12-month-old transplanted mice (WT, n = 17; Mafb −/−, n = 12). The data are presented as the mean ± s.e.m. *p < 0.05 (Welch’s t-test). The results of two independent experiments were pooled