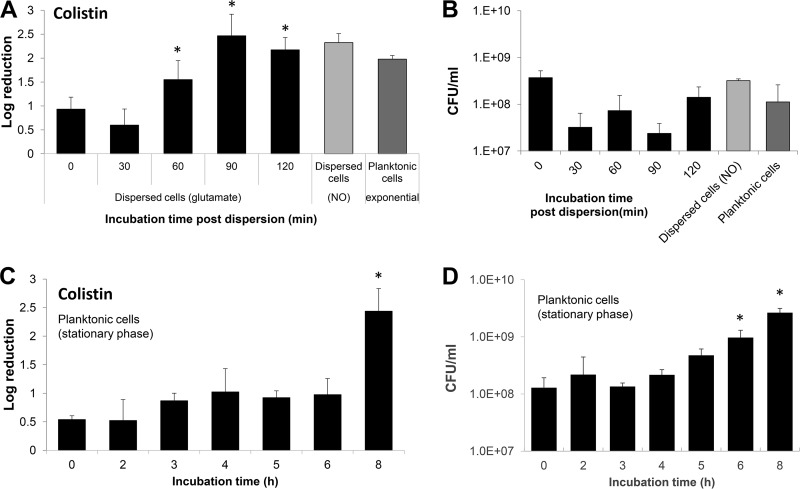
FIG 3.
Susceptibility of dispersed and stationary-phase cells to colistin after recovery in fresh medium under planktonic growth conditions. (A and B) Dispersed cells obtained in response to glutamate were collected, washed, resuspended in fresh VBMM, adjusted to an OD of 0.2, and subsequently allowed to grow at 22°C with aeration. At the times indicated, the cells were split into equal volumes and either left untreated or exposed to colistin (20 μg/ml) for 1 h at 37°C. (A) Susceptibility phenotype of dispersed cells and after recovery for up to 2 h under planktonic growth conditions to colistin. Colistin susceptibility is expressed as log10 reduction in CFU. (B) Average number of viable cells, expressed as CFU, present in dispersed cells at the time of recovery and over the course of 2 h under planktonic growth conditions. (C and D) Planktonic cells grown for 24 h were washed, resuspended in fresh VBMM medium, adjusted to an OD of 0.2, and subsequently allowed to grow at 22°C with aeration. At the times indicated, the cells were split into equal volumes and either left untreated or exposed to colistin (20 μg/ml) for 1 h at 37°C. (C) Susceptibility phenotype of stationary-phase cells and after growth under planktonic growth conditions in fresh VBMM to colistin. Colistin susceptibility is expressed as log10 reduction in CFU. (B) Average number of viable cells, expressed as CFU, present in stationary-phase cells at the time of recovery and over the course of 8 h under planktonic growth conditions. Experiments were repeated at least three times. Error bars indicate standard deviations. *, Significantly different from glutamate-dispersed cells at 0 min (P < 0.01 as determined by ANOVA and SigmaStat).